Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Phases of Matter
The phases of matter refer to the distinct forms that different phases of matter take on. The most common phases are solid, liquid, and gas, which are determined by the arrangement and energy of particles. Understanding these phases is crucial for identifying the standard states of elements and compounds at a given temperature and pressure.
Recommended video:
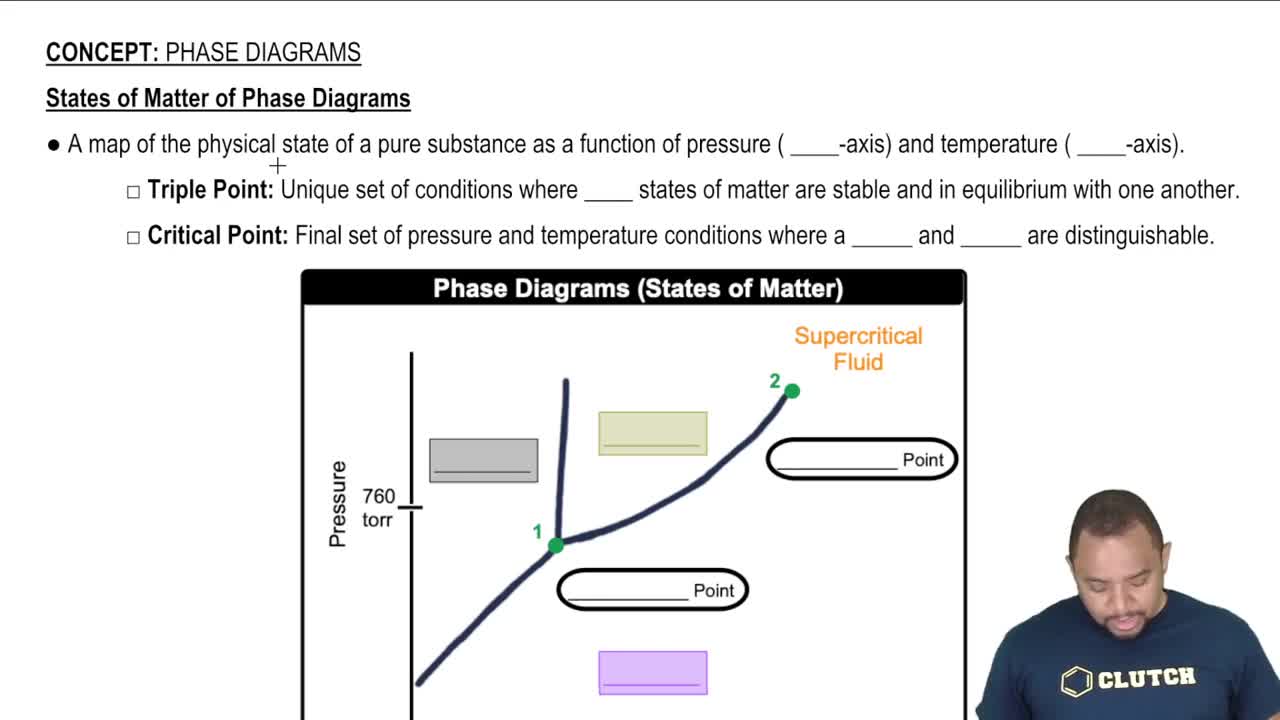
States of Matter of Phase Diagrams
Standard State
The standard state of a substance is defined as its most stable physical form at a specified temperature (usually 25°C) and pressure (1 atm). This concept is essential for determining the phase of matter for elements and compounds, as it provides a reference point for their physical properties under standard conditions.
Recommended video:
Standard Reduction Potentials
Element and Compound Properties
Elements and compounds exhibit specific properties that dictate their phase at standard conditions. For example, some elements like chlorine (Cl2) are gases, while others like mercury (Hg) are liquids at room temperature. Understanding these properties helps in predicting the phase of various substances based on their molecular structure and intermolecular forces.
Recommended video: