Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
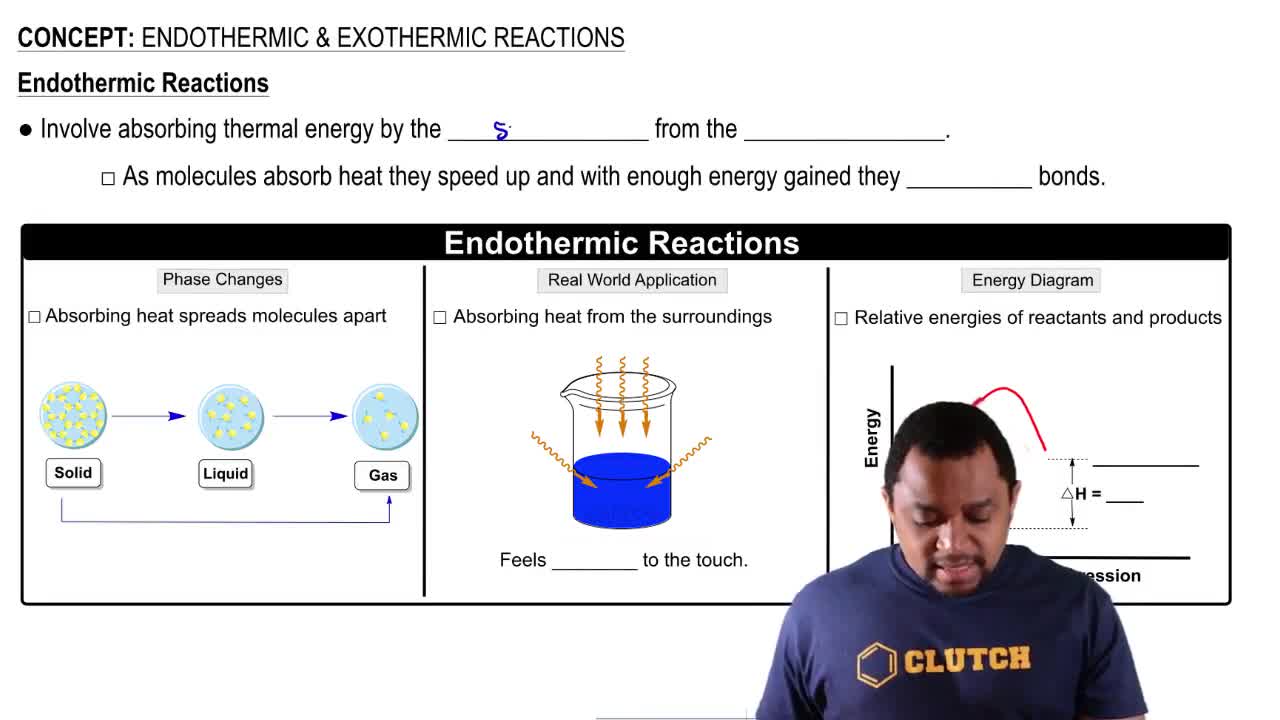
Endothermic Reactions
Endothermic reactions absorb heat from their surroundings, resulting in a decrease in temperature. In the case of the cold pack, the dissolution of NH4NO3 is an endothermic process, which means it requires energy to break the ionic bonds in the solid, leading to a cooling effect. This concept is crucial for understanding why the temperature drops when the pack is activated.
Recommended video:
Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
Specific Heat Capacity
Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree Celsius. For the solution in the cold pack, the specific heat is given as 4.18 J/(g°C). This property is essential for calculating how much the temperature of the solution will change when a certain amount of heat is absorbed during the dissolution of NH4NO3.
Recommended video:
Heat Transfer and Conservation of Energy
The principle of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed. In the context of the cold pack, the heat absorbed by the dissolution of NH4NO3 must equal the heat lost by the water in the pack. This relationship allows us to set up an equation to find the final temperature of the solution after the cold pack is activated.
Recommended video:
Law of Conservation of Mass