Textbook Question
Characterize bonds between the two atoms as covalent or ionic.
(a) Cl and F
(b) Rb and F
(c) Na and S
(d) N and S
522
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
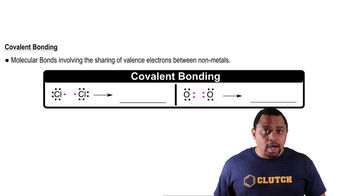

What general trends in electronegativity occur in the periodic table?
Predict the electronegativity of the undiscovered element with Z = 119.