Textbook Question
Compare and contrast the properties of ammonia and phosphine.
101
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
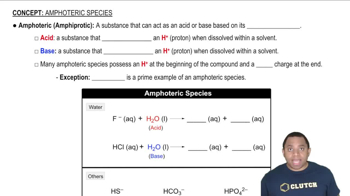


Compare and contrast the properties of ammonia and phosphine.
In what forms is oxygen commonly found in nature?
Arrange the following oxides in order of increasing basic character: Al2O3, Cs2O, K2O, N2O5.
Write a balanced net ionic equation for the reaction of the amphoteric oxide Ga2O3 with:
a. Aqueous sulfuric acid
a. Why is the SO3 molecule trigonal planar but the SO32– ion is trigonal pyramidal?
Give one example from main-group chemistry that illustrates each of the following descriptions.
d. Polar molecule that violates the octet rule