Arrange the following oxides in order of increasing basic character: Al2O3, Cs2O, K2O, N2O5.
Ch.22 - The Main Group Elements
Chapter 22, Problem 22.141a
a. Why is the SO3 molecule trigonal planar but the SO32– ion is trigonal pyramidal?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Determine the number of valence electrons for each species: SO_3 and SO_3^{2-}.
For SO_3, sulfur (S) has 6 valence electrons and each oxygen (O) has 6 valence electrons, totaling 24 valence electrons.
For SO_3^{2-}, add 2 extra electrons to the total from SO_3 due to the 2- charge, resulting in 26 valence electrons.
Draw the Lewis structures for both SO_3 and SO_3^{2-}, ensuring to distribute electrons to satisfy the octet rule where possible.
Use VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry: SO_3 has no lone pairs on the central sulfur, resulting in a trigonal planar shape, while SO_3^{2-} has one lone pair on sulfur, leading to a trigonal pyramidal shape.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
0m:0sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It is determined by the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons around the central atom, which influence the shape due to repulsion between electron pairs. Understanding molecular geometry is crucial for predicting the physical and chemical properties of substances.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Molecular Geometry with Two Electron Groups
VSEPR Theory
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a model used to predict the geometry of individual molecules based on the repulsion between electron pairs in the valence shell of the central atom. According to VSEPR, electron pairs will arrange themselves to minimize repulsion, leading to specific molecular shapes, such as trigonal planar or trigonal pyramidal.
Recommended video:
Guided course
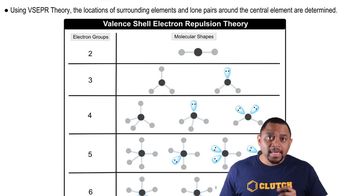
Molecular Shapes and VSEPR
Formal Charge and Ion Stability
Formal charge is a concept used to determine the distribution of electrons in a molecule or ion, helping to assess its stability. In the case of the SO3 molecule and the SO3^2– ion, the formal charge influences the arrangement of electrons and the resulting molecular shape. Understanding formal charge is essential for predicting the behavior of ions and their geometries.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Formal Charge
Related Practice
Textbook Question
106
views
Textbook Question
Write a balanced net ionic equation for the reaction of the amphoteric oxide ZnO with:
a. Hydrochloric acid
83
views
Textbook Question
Write a balanced net ionic equation for the reaction of the amphoteric oxide Ga2O3 with:
a. Aqueous sulfuric acid
72
views
Textbook Question
Give one example from main-group chemistry that illustrates each of the following descriptions.
d. Polar molecule that violates the octet rule
106
views
Textbook Question
An important physiological reaction of nitric oxide (NO) is its interaction with the superoxide ion (O2–) to form the peroxynitrite ion (ONOO–).
a. Write electron-dot structures for NO, O2–, and ONOO–, and predict the O–N–O bond angle in ONOO–.
101
views
Textbook Question
Locate each of the following elements on the periodic table.
(f) Group 5A element that forms the strongest p bonds
110
views
