Which of the group 4A elements have allotropes with the diamond structure? Which have metallic allotropes? How does the variation in the structure of the group 4A elements illustrate how metallic character varies down a periodic group?
Ch.22 - The Main Group Elements
Chapter 22, Problem 22.99
Using the shorthand notation of Figure 22.9, draw the structure of the silicate anion in:
(a) K4SiO4 (b) Ag10Si4O13
What is the relationship between the charge on the anion and the number of terminal O atoms?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the silicate anion in each compound. For (a) K_4SiO_4, the silicate anion is SiO_4^{4-}. For (b) Ag_{10}Si_4O_{13}, the silicate anion is Si_4O_{13}^{10-}.
Determine the structure of the silicate anion. The SiO_4^{4-} anion is a tetrahedral structure with one silicon atom at the center and four oxygen atoms at the corners.
For Si_4O_{13}^{10-}, recognize that it is a combination of four SiO_4 tetrahedra sharing oxygen atoms. Identify the number of shared and terminal oxygen atoms.
Count the terminal oxygen atoms in each silicate anion. In SiO_4^{4-}, all four oxygen atoms are terminal. In Si_4O_{13}^{10-}, determine how many oxygen atoms are terminal by considering the shared oxygen atoms.
Relate the charge on the anion to the number of terminal oxygen atoms. Note that each terminal oxygen contributes a -1 charge, and shared oxygen atoms contribute less to the overall charge.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
0m:0sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Silicate Anions
Silicate anions are polyatomic ions composed of silicon and oxygen, typically represented in various structural forms. The basic unit is the silica tetrahedron (SiO4) where a silicon atom is surrounded by four oxygen atoms. These anions can combine in different ways to form larger structures, influencing their chemical properties and reactivity.
Recommended video:
Guided course
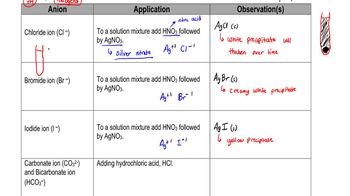
Test for Anions
Coordination and Charge Balance
In silicate structures, the coordination of silicon and oxygen atoms determines the overall charge of the anion. Each terminal oxygen atom typically carries a negative charge, contributing to the anion's total charge. Understanding how these charges balance with cations in compounds like K4SiO4 and Ag10Si4O13 is crucial for predicting stability and reactivity.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Coordination Complexes Example
Structural Representation
The shorthand notation for silicate structures simplifies the representation of complex silicate anions. This notation often uses symbols to denote silicon and oxygen atoms, along with lines to indicate bonds. Familiarity with this notation is essential for accurately drawing and interpreting the structures of silicate compounds, as well as understanding their relationships with cations.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Resonance Structures
Related Practice
Textbook Question
87
views
Textbook Question
Give an example of an ionic carbide. What is the oxidation state of carbon in this substance?
84
views
Textbook Question
Why are CO and CN– so toxic to humans?
109
views
Textbook Question
The following pictures represent structures of the hydrides of four second-row elements:
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(c) Which compounds yield H2 gas when they are mixed together?
99
views
Textbook Question
In the following pictures of oxides, red spheres represent O atoms or ions, and green spheres represent atoms or ions of a second- or third-row element in its highest oxidation state.
(1)
(2)
(3)
(b) Identify each oxide as ionic or covalent.
105
views
Textbook Question
Look at the location of elements A, B, C, and D in the following periodic table:
(a) Write the formula of the oxide that has each of these elements in its highest oxidation state.
109
views
