Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Beta Emission
Beta emission is a type of radioactive decay in which a neutron in an unstable nucleus is transformed into a proton, emitting a beta particle (an electron) in the process. This transformation increases the atomic number of the element by one, as the number of protons in the nucleus increases, resulting in a new element that is one position higher on the periodic table.
Recommended video:
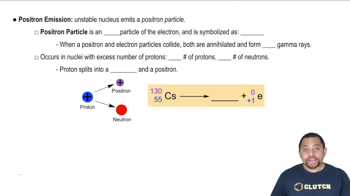
Positron Emission
Positron emission, or beta plus decay, occurs when a proton in an unstable nucleus is converted into a neutron, releasing a positron (the antimatter counterpart of an electron). This process decreases the atomic number of the element by one, as the number of protons decreases, leading to the formation of a new element that is one position lower on the periodic table.
Recommended video:
Atomic Number
The atomic number of an element is defined as the number of protons in its nucleus, which determines the element's identity and its position in the periodic table. Changes in the atomic number due to nuclear reactions, such as beta and positron emissions, directly affect the chemical properties of the resulting element, as it alters the number of protons and, consequently, the electron configuration.
Recommended video: