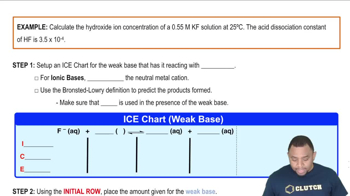
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lewis Acids and Bases
Lewis acids are substances that can accept an electron pair, while Lewis bases are those that can donate an electron pair. This definition expands the traditional Brønsted-Lowry concept of acids and bases, which focuses on proton transfer. Understanding this distinction is crucial for classifying chemical species based on their electron pair interactions.
Recommended video:
Electron Pair Donation
A Lewis base is characterized by its ability to donate a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. In the case of hydroxide ion (OH-), it has a lone pair of electrons that it can readily donate, making it a strong Lewis base. This property is essential for predicting how OH- will interact with Lewis acids in chemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
Hydroxide Ion (OH-)
The hydroxide ion (OH-) is a negatively charged ion consisting of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. It is commonly encountered in aqueous solutions and is known for its basic properties. Recognizing OH- as a Lewis base is important for understanding its role in acid-base chemistry and its interactions with various Lewis acids.
Recommended video:
Hydroxide Ion Concentration Example