 Back
BackProblem 65a,b
Identify the stronger base in each of the following pairs.
Explain your reasoning.
(a) ClO2- or ClO3-
(b) HSO4- or HSeO4-
- Which of the following is a Brønsted-Lowry base, but not an Arrhenius base? (LO 16.1) (a) HNO3 (b) CsOH (c) CH3NH2 (d) CH3OH
Problem 1
- The following pictures represent equal volumes of aqueous solutions of three acids HA (A = X, Y, or Z); water molecules have been omitted for clarity. Which is the strongest acid?
Problem 2
(a) HX (b) HY (c) HZ (d) All three acids are strong acids and have equal strength.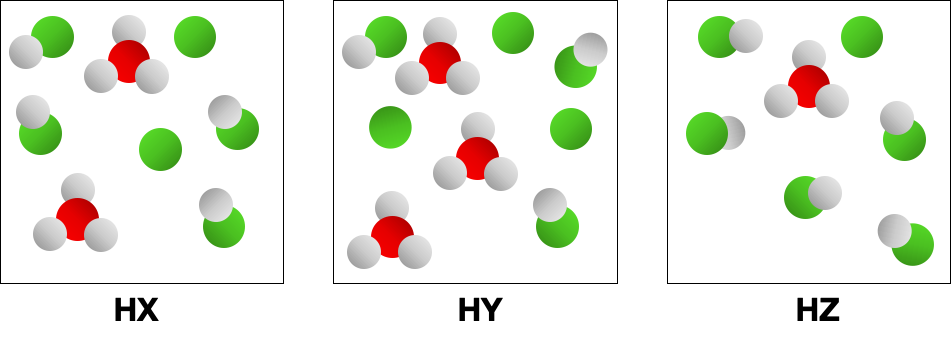
- Consider the conjugate bases, 1X-, Y-, Z-2 in Problem 2. If you mix equal concentrations of reactants and products, which of the following reactions will proceed to the left? (LO 16.3) (a) HX + Y- HY + X- (b) HX + Z- HZ + X- (c) HY + X- HX + Y- (d) HZ + Y- HY + Z-
Problem 3

- Which is the strongest acid? (LO 16.4) (a) HClO3 (b) HBrO3 (c) H2SO3 (d) H2TeO3
Problem 4
- What is the concentration of hydroxide ions 3OH-4 in a glass of wine with pH = 3.64? (LO 16.5, 16.6) (a) 2.3 * 10-4 M (b) 6.4 * 10-3 M (c) 6.8 * 10-9 M (d) 4.4 * 10-11 M
Problem 5
- What is the pH of an aqueous solution of Ca1OH22 at 25.0 °C with a concentration of 6.3 * 10-5 M? (LO 16.7) (a) 4.20 (b) 10.10 (c) 11.36 (d) 9.80
Problem 6
- An acid solution with a concentration of 0.500 M has a pH = 3.21. What is the Ka of the acid? (LO 16.8) (a) 1.2 * 10-5 (b) 1.7 * 10-6 (c) 7.6 * 10-7 (d) 5.4 * 10-3
Problem 7
- Determine the following concentrations for a 0.40 M H2Se solution that has the stepwise dissociation constants of Ka1 = 1.3 * 10^-4 and Ka2 = 1.0 * 10^-11. (LO 16.10) (a) [H2Se] = 0.35, [HSe^-] = 5.0 * 10^-2, [H3O^+] = 3.0 * 10^-3, [Se^2-] = 1.3 * 10^-4 (b) [H2Se] = 0.39, [HSe^-] = 7.2 * 10^-3, [H3O^+] = 7.2 * 10^-3, [Se^2-] = 1.0 * 10^-11 (c) [H2Se] = 0.31, [HSe^-] = 9.0 * 10^-2, [H3O^+] = 9.0 * 10^-2, [Se^2-] = 1.0 * 10^-11 (d) [H2Se] = 0.40, [HSe^-] = 1.3 * 10^-4, [H3O^+] = 1.3 * 10^-4, [Se^2-] = 1.0 * 10^-11
Problem 9
- Ammonia 1NH32 has base dissociation constant 1Kb2 of 1.8 * 10-5. What is the concentration of an aqueous ammonia solution that has a pH of 11.68? (LO 16.11) (a) 0.28 M (b) 3.6 M (c) 9.0 * 10-3 M (d) 1.3 M
Problem 10
- Using values of Kb in Appendix C, calculate values of Ka for each of the following ions: (b) Hydroxylammonium ion, NH3OH+; (c) Anilinium ion, C6H5NH3+; (d) Pyridinium ion, C5H5NH+.
Problem 12
- Consider the reaction: SO2 + OH- S HSO3 -. Which reaction scheme shows the correct use of the curved arrow notation representing the donation of an electron pair and the correct labeling of the Lewis acid and Lewis base? (LO 16.14) (a) (b) (c) (d)
Problem 13
- For each of the Lewis acid–base reactions in Problem 16.138, draw electron-dot structures for the reactants and products, and use the curved arrow notation to represent the donation of a lone pair of electrons from the Lewis base to the Lewis acid.
Problem 14
- For a solution of two weak acids with comparable values of Ka, there is no single principal reaction. The two acid dissociation equilibrium equations must therefore be solved simultaneously. Calculate the pH in a solution that is 0.10 M in acetic acid (CH3CO2H, Ka = 1.8 * 10^-5) and 0.10 M in benzoic acid (C6H5CO2H, Ka = 6.5 * 10^-5). (Hint: Let x = [CH3CO2H] that dissociates and y = [C6H5CO2H] that dissociates; then [H3O+] = x + y.)
Problem 15
Problem 16-145
What is the pH and the principal source of H3O+ ions in 1.0 * 10-10 M HCl? (Hint: The pH of an acid solution can’t exceed 7.) What is the pH of 1.0 * 10-7 M HCl?
Problem 16.85
Calculate the pH of solutions prepared by:
(d) Mixing equal volumes of 0.20 M HCl and 0.50 M HNO3.
(Assume that volumes are additive.)
Problem 17.142
The acidity of lemon juice is derived primarily from citric acid (H3Cit), a triprotic acid. What are the concentrations of H3Cit, H2Cit-, HCit2-, and Cit3- in a sample of lemon juice that has a pH of 2.37 and a total concentration of the four citrate-containing species of 0.350 M?
Problem 17-143a
A 100.0 mL sample of a solution that is 0.100 M in HCl and 0.100 M in HCN is titrated with 0.100 M NaOH. Calculate the pH after the addition of the following volumes of NaOH:
(a) 0.0 mL
Problem 17-148e
A 40.0 mL sample of a mixture of HCl and H3PO4 was titrated with 0.100 M NaOH. The first equivalence point was reached after 88.0 mL of base, and the second equivalence point was reached after 126.4 mL of base.
(e) Sketch the pH titration curve, and label the buffer regions and equivalence points.
Problem 39c
The following pictures represent aqueous solutions of three acids HA1A = X, Y, or Z2; water molecules have been omitted for clarity.

(c) Which acid, if any, is a strong acid?
Problem 39e
The following pictures represent aqueous solutions of three acids HA1A = X, Y, or Z2; water molecules have been omitted for clarity.

(e) What is the percent dissociation in the solution of HZ?
- Locate sulfur, selenium, chlorine, and bromine in the periodic table: (a) Which binary acid 1H2S, H2Se, HCl, or HBr2 is the strongest? Which is the weakest? Explain.
Problem 40
Problem 41
Which of the following pictures represents a solution of a weak diprotic acid, H2A? (Water molecules have been omitted for clarity.) Which pictures represent an impossible situation? Explain.

(a) (b) (c) (d)
Problem 43a
The following pictures represent solutions of three salts NaA (A- = X-, Y-, or Z-); water molecules and Na+ ions have been omitted for clarity.
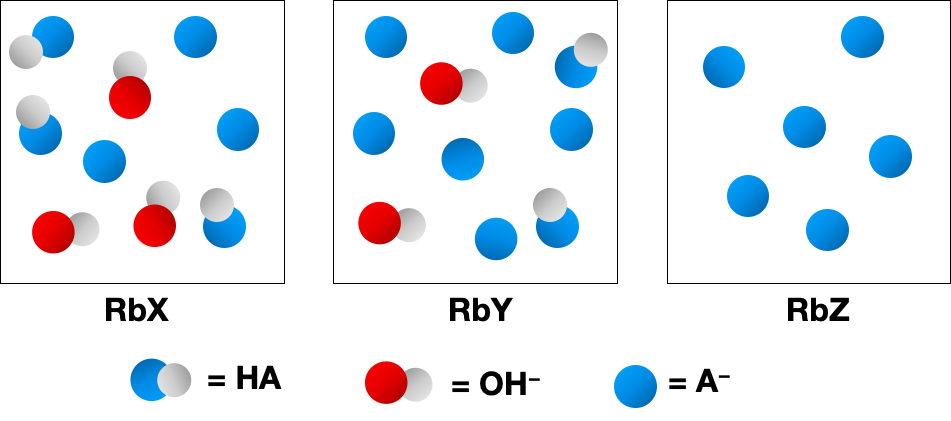
(a) Arrange the three A- anions in order of increasing base strength.
Problem 43b
The following pictures represent solutions of three salts NaA (A- = X-, Y-, or Z-); water molecules and Na+ ions have been omitted for clarity.

(b) Which A- anion has the strongest conjugate acid?
Problem 43c
The following pictures represent solutions of three salts NaA (A- = X-, Y-, or Z-); water molecules and Na+ ions have been omitted for clarity.

(c) Which A- anion has the smallest value of pKb?
Problem 44a
The following picture represents the hydrated metal cation M1H2O26 n + , where n = 1, 2, or 3.

(a) Write a balanced equation for the reaction of M1H2O26 n + with water and write the equilibrium equation for the reaction.
Problem 44b
The following picture represents the hydrated metal cation M1H2O26 n + , where n = 1, 2, or 3.
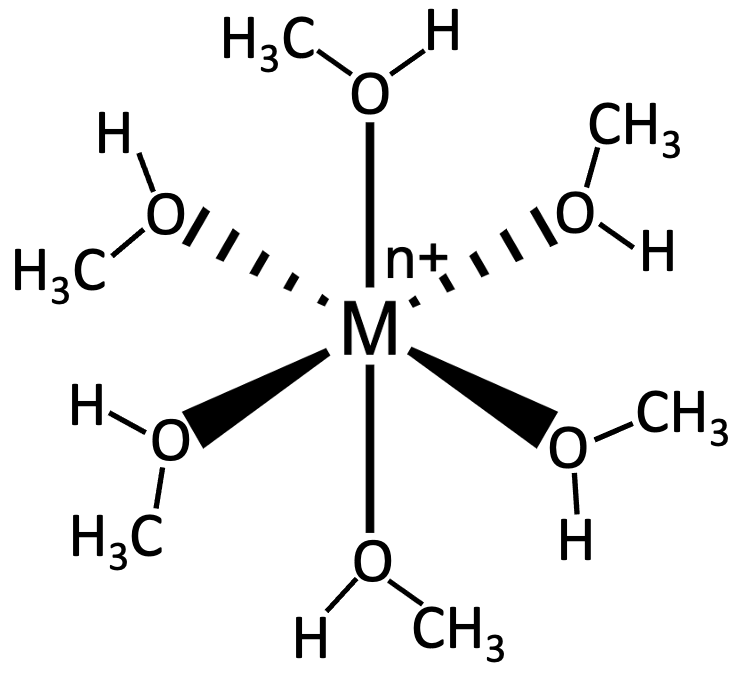
(b) Does the equilibrium constant increase, decrease, or remain the same as the value of n increases? Explain.
Problem 44c
The following picture represents the hydrated metal cation M1H2O26 n + , where n = 1, 2, or 3. (c) Which M1H2O26n + ion 1n = 1,2, or 32 is the strongest acid, and which has the strongest conjugate base?
- Look at the electron-dot structures of the following molecules and ions: (b) Which can behave as a Lewis acid? Which can behave as a Lewis base?
Problem 45

