Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
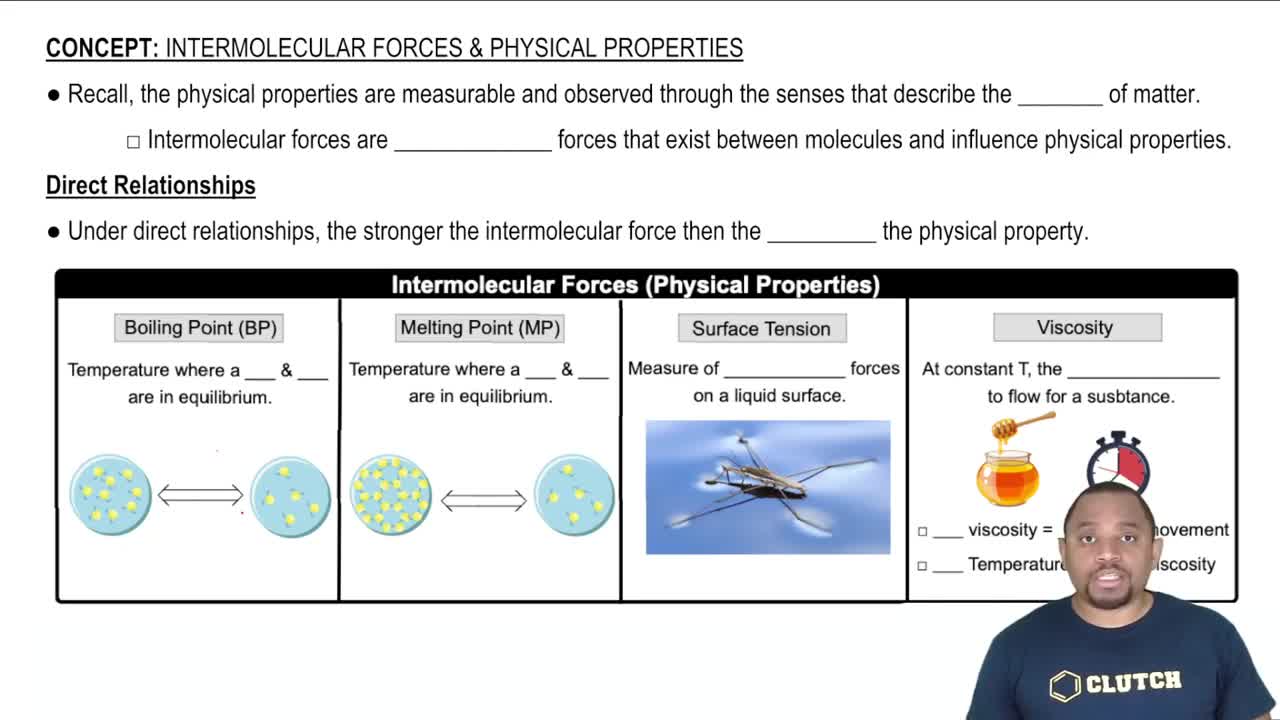
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow. It describes how thick or thin a liquid is; for example, water has a low viscosity, allowing it to flow easily, while maple syrup has a high viscosity, making it flow more slowly. The difference in viscosity between these two liquids is a primary factor in their flow rates through narrow openings.
Recommended video:
Intermolecular Forces and Properties
Surface Tension
Surface tension is the cohesive force at the surface of a liquid that causes it to behave like a stretched elastic membrane. It arises from the attraction between molecules at the surface and can affect how liquids interact with their environment. While surface tension influences droplet formation and the ability of liquids to wet surfaces, it is less significant than viscosity in determining flow rates through narrow openings.
Recommended video:
Intermolecular Forces and Properties
Fluid Dynamics
Fluid dynamics is the study of how fluids (liquids and gases) move and the forces acting on them. It encompasses principles such as flow rate, viscosity, and pressure, which are essential for understanding the behavior of different liquids in various conditions. In the context of the question, fluid dynamics helps explain why water flows quickly compared to the slower flow of maple syrup, primarily due to differences in viscosity.
Recommended video:
States of Matter of Phase Diagrams