Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Phase Transitions
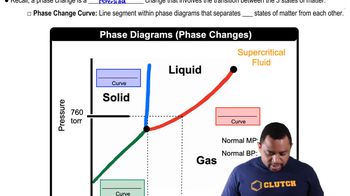
Phase transitions refer to the changes in the state of matter, such as solid, liquid, and gas, that occur due to variations in temperature or pressure. In this context, the compound transitions from solid to smectic liquid crystal at 121 °C and then to a liquid phase at 131 °C. Understanding these transitions is crucial for predicting molecular arrangements at specific temperatures.
Recommended video:
Phase Changes in Diagrams
Liquid Crystal Phases
Liquid crystals are substances that exhibit properties between those of conventional liquids and solid crystals. The smectic phase, mentioned in the question, is characterized by layered structures where molecules are arranged in parallel layers, allowing for some fluidity. Recognizing the characteristics of different liquid crystal phases helps in visualizing molecular arrangements at various temperatures.
Recommended video:
Phase Changes in Diagrams
Molecular Arrangement
Molecular arrangement refers to the specific organization of molecules within a phase. At 125 °C, which is between the smectic and liquid phases, the arrangement will reflect properties of both states. Analyzing the provided image of the liquid phase at 135 °C can help infer the likely arrangement at 125 °C, as the molecules will still exhibit some ordered structure typical of liquid crystals.
Recommended video: