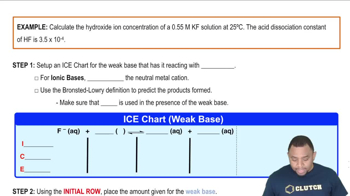
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are formed when atoms transfer electrons, resulting in the formation of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. These oppositely charged ions attract each other, creating a stable compound. Understanding the nature of ionic bonds is essential for naming and writing formulas for these compounds.
Recommended video:
Nomenclature of Ionic Compounds
The nomenclature of ionic compounds involves specific rules for naming the cations and anions. Typically, the cation retains its elemental name, while the anion's name is derived from its elemental name, often modified to end in '-ide' for simple anions. For transition metals, the oxidation state is indicated using Roman numerals.
Recommended video:
Hydroxide Ion
The hydroxide ion (OH⁻) is a polyatomic ion consisting of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom, carrying a negative charge. It is commonly found in bases and plays a crucial role in the naming of compounds that contain it, such as hydroxides. Recognizing hydroxide's presence is vital for accurately naming compounds like Cu(OH)₂.
Recommended video:
Hydroxide Ion Concentration Example
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance