Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are formed from the electrostatic attraction between cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions). They typically consist of a metal and a non-metal, where the metal donates electrons to become a cation, while the non-metal accepts electrons to become an anion. Understanding the composition of ionic compounds is essential for identifying the charges of the ions involved.
Recommended video:
Oxidation States
The oxidation state of an element in a compound indicates the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of that element. In ionic compounds, the oxidation states help determine the charges of the cations and anions. For example, cobalt (Co) can have multiple oxidation states, which affects the charge of the cation in the compound Co(OH)2, where hydroxide (OH) has a charge of -1.
Recommended video:
Hydroxide Ion
The hydroxide ion (OH-) is a common anion in many ionic compounds, consisting of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom, carrying a -1 charge. In the compound Co(OH)2, two hydroxide ions balance the charge of the cobalt cation. Recognizing the charge and composition of hydroxide is crucial for determining the overall charge balance in ionic compounds.
Recommended video:
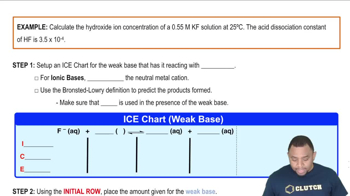
Hydroxide Ion Concentration Example
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance