Consider the molecular models shown here, where X represents a halogen atom. (a) If X is the same atom in both molecules, which molecule will be more acidic?
Ch.16 - Acid-Base Equilibria
Chapter 16, Problem 14
Which of the following statements is false? (a) An Arrhenius base increases the concentration of OH- in water. (b) A Brønsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor. (c) Water can act as a Brønsted–Lowry acid. (d) Water can act as a Brønsted–Lowry base. (e) Any compound that contains an –OH group acts as a Brønsted-Lowry base.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the definitions of Arrhenius and Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases.
Recall that an Arrhenius base increases the concentration of OH^- ions in water.
Understand that a Brønsted-Lowry base is defined as a proton (H^+) acceptor.
Recognize that water (H2O) can act as both a Brønsted-Lowry acid (proton donor) and a Brønsted-Lowry base (proton acceptor).
Evaluate the statement that any compound with an –OH group acts as a Brønsted-Lowry base, and consider exceptions such as alcohols, which do not typically act as bases.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Arrhenius Theory of Acids and Bases
The Arrhenius theory defines acids as substances that increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous solution, while bases increase the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-). This theory is foundational in understanding the behavior of acids and bases in water, particularly in identifying how they dissociate and interact in solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Arrhenius Acids and Bases
Brønsted-Lowry Theory of Acids and Bases
The Brønsted-Lowry theory expands the definition of acids and bases beyond aqueous solutions. According to this theory, an acid is a proton donor and a base is a proton acceptor. This concept allows for a broader understanding of acid-base reactions, including those that occur in non-aqueous environments.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Bronsted-Lowry Acid-Base Theory
Amphoteric Substances
Amphoteric substances are those that can act as either an acid or a base depending on the context of the reaction. Water is a prime example, as it can donate a proton (acting as an acid) or accept a proton (acting as a base). Understanding this dual behavior is crucial for analyzing reactions involving water and other amphoteric compounds.
Recommended video:
Guided course
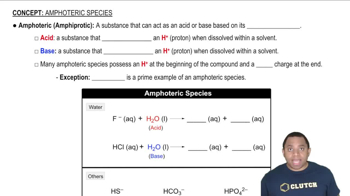
Amphoteric Species
Related Practice
Textbook Question
412
views
Textbook Question
Consider the molecular models shown here, where X represents a halogen atom. (b) Does the acidity of each molecule increase or decrease as the electronegativity of the atom X increases?
330
views
Textbook Question
NH31g2 and HCl(g) react to form the ionic solid NH4Cl1s2. Which substance is the Brønsted–Lowry acid in this reaction? Which is the Brønsted–Lowry base?
359
views
Textbook Question
Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base among the reactants in each of the following reactions: (d) HIO1lq2 + NH2-1lq2 Δ NH31lq2 + IO-1lq2(lq denotes liquid ammonia as solvent)
473
views
Textbook Question
Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base in each of the following reactions: (b) FeBr31s2 + Br-1aq2 Δ FeBr4-1aq2
1152
views
Textbook Question
Give the conjugate base of the following Brønsted–Lowry acids: (i) HIO3, (ii) NH4+.
413
views
