Calculate 3OH-4 for each of the following solutions, and indicate whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral: (c) a solution in which 3H+4 is 1000 times greater than 3OH-4.
The average pH of normal arterial blood is 7.40. At normal body temperature 137 °C2, Kw = 2.4 * 10-14. Calculate 3H+4, 3OH-4, and pOH for blood at this temperature.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
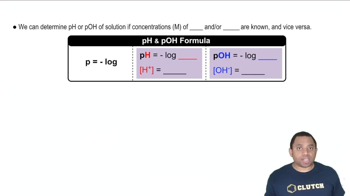
pH and pOH
Ion Product of Water (Kw)

Calculating Ion Concentrations

Deuterium oxide 1D2O, where D is deuterium, the hydrogen-2 isotope) has an ion-product constant, Kw, of 8.9 * 10-16 at 20 °C. Calculate 3D+4 and 3OD-4 for pure (neutral) D2O at this temperature.
By what factor does 3H+4 change for a pH change of (a) 2.00 units?
Addition of the indicator methyl orange to an unknown solution leads to a yellow color. The addition of bromthymol blue to the same solution also leads to a yellow color. (b) What is the range (in whole numbers) of possible pH values for the solution?
Addition of phenolphthalein to an unknown colorless solution does not cause a color change. The addition of bromthymol blue to the same solution leads to a yellow color. (b) Which of the following can you establish about the solution: (i) A minimum pH, (ii) A maximum pH, or (iii) A specific range of pH values?
Addition of phenolphthalein to an unknown colorless solution does not cause a color change. The addition of bromthymol blue to the same solution leads to a yellow color. (c) What other indicator or indicators would you want to use to determine the pH of the solution more precisely?
