Write a chemical equation that illustrates the autoionization of water.
Ch.16 - Acid-Base Equilibria
Chapter 16, Problem 34a
Calculate 3OH-4 for each of the following solutions, and indicate whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral: (a) 3H+4 = 0.0505 M
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the given concentration: \([H^+] = 0.0505\, \text{M}\).
Use the relationship between \([H^+]\) and \([OH^-]\) in water: \([H^+][OH^-] = 1.0 \times 10^{-14}\, \text{at 25°C}\).
Rearrange the equation to solve for \([OH^-]\): \([OH^-] = \frac{1.0 \times 10^{-14}}{[H^+]}\).
Substitute the given \([H^+]\) value into the equation: \([OH^-] = \frac{1.0 \times 10^{-14}}{0.0505}\, \text{M}\).
Determine if the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral by comparing \([H^+]\) and \([OH^-]\): If \([H^+] > [OH^-]\), the solution is acidic; if \([H^+] < [OH^-]\), it is basic; if \([H^+] = [OH^-]\), it is neutral.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
pH and pOH
pH is a measure of the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution, indicating its acidity or basicity. The pOH is similarly a measure of hydroxide ion concentration. The relationship between pH and pOH is defined by the equation pH + pOH = 14 at 25°C. Understanding these concepts is essential for determining the nature of a solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course
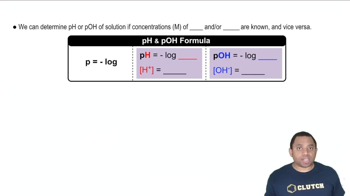
pH and pOH Calculations
Acidic, Basic, and Neutral Solutions
A solution is considered acidic if its pH is less than 7, basic if its pH is greater than 7, and neutral if its pH is exactly 7. The concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-) in a solution determines its classification. For example, a higher concentration of H+ indicates acidity, while a higher concentration of OH- indicates basicity.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Balancing Basic Redox Reactions
Calculating pOH from pH
To find the pOH from a given concentration of H+, one first calculates the pH using the formula pH = -log[H+]. Once the pH is determined, pOH can be calculated using the relationship pOH = 14 - pH. This calculation is crucial for determining the hydroxide ion concentration and the overall nature of the solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

pH and pOH Calculations
Related Practice
Textbook Question
572
views
Textbook Question
Write the expression for the ion product constant for water, Kw.
645
views
Textbook Question
Calculate 3H+4 for each of the following solutions, and indicate whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral: (b) 3OH-4 = 8.8 * 10-9 M
375
views
Textbook Question
Calculate 3OH-4 for each of the following solutions, and indicate whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral: (b) 3H+4 = 2.5 * 10-10 M
394
views
Textbook Question
Calculate 3OH-4 for each of the following solutions, and indicate whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral: (c) a solution in which 3H+4 is 1000 times greater than 3OH-4.
339
views
Textbook Question
Deuterium oxide 1D2O, where D is deuterium, the hydrogen-2 isotope) has an ion-product constant, Kw, of 8.9 * 10-16 at 20 °C. Calculate 3D+4 and 3OD-4 for pure (neutral) D2O at this temperature.
2283
views
