Sulfur tetrafluoride (SF4) reacts slowly with O2 to form sulfur tetrafluoride monoxide (OSF4) according to the following unbalanced reaction: SF4(g) + O2(g) → OSF4(g) The O atom and the four F atoms in OSF4 are bonded to a central S atom. (c) Use average bond enthalpies (Table 8.3) to estimate the enthalpy of the reaction. Is it endothermic or exothermic?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
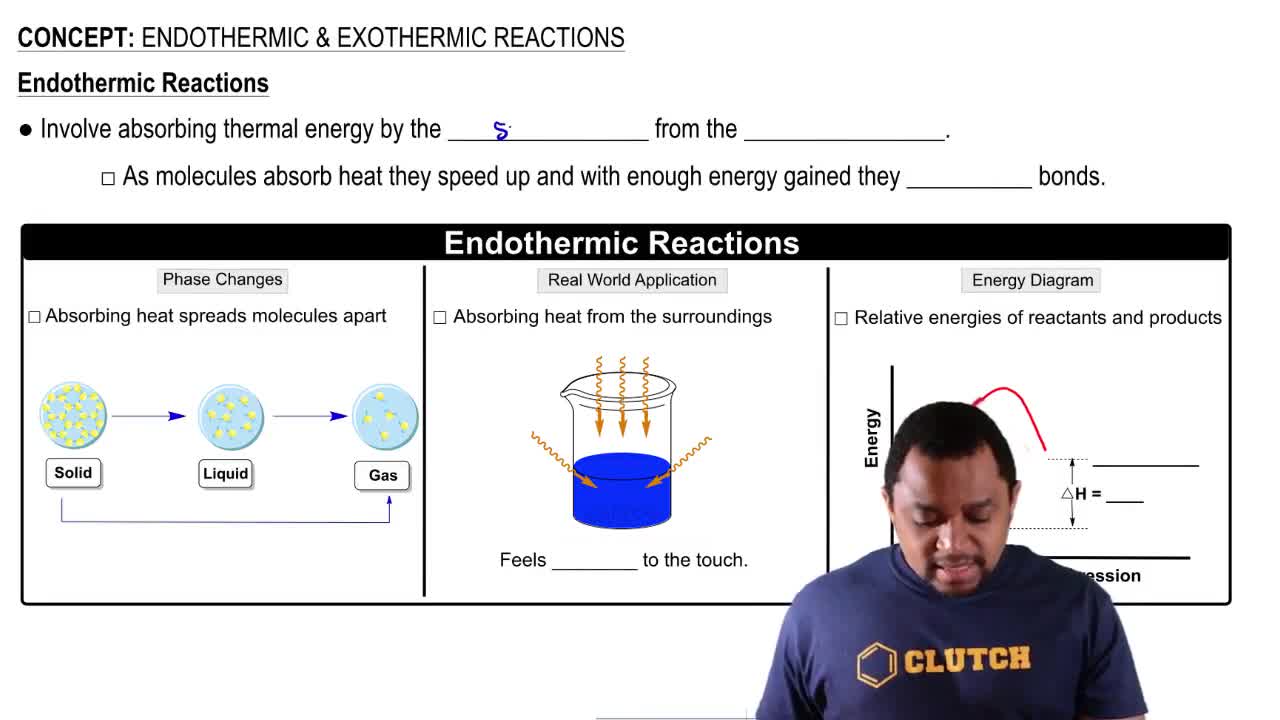
Bond Enthalpy

Enthalpy Change (ΔH)

Exothermic vs. Endothermic Reactions
Sulfur tetrafluoride 1SF42 reacts slowly with O2 to form sulfur tetrafluoride monoxide 1OSF42 according to the following unbalanced reaction: SF41g2 + O21g2¡OSF41g2 The O atom and the four F atoms in OSF4 are bonded to a central S atom. (a) Balance the equation.
Sulfur tetrafluoride (SF4) reacts slowly with O2 to form sulfur tetrafluoride monoxide (OSF4) according to the following unbalanced reaction: SF4(g) + O2(g) → OSF4(g) The O atom and the four F atoms in OSF4 are bonded to a central S atom. (b) Write a Lewis structure of OSF4 in which the formal charges of all atoms are zero.
Sulfur tetrafluoride 1SF42 reacts slowly with O2 to form sulfur
tetrafluoride monoxide 1OSF42 according to the following
unbalanced reaction:
SF41g2 + O21g2¡OSF41g2
The O atom and the four F atoms in OSF4 are bonded to a
central S atom.
(e) For each of the molecules you drew in part (d), state how many
fluorines are equatorial and how many are axial.
