The orbital diagram that follows presents the final step in the formation of hybrid orbitals by a silicon atom. (a) Which of the following best describes what took place before the step pictured in the diagram: (i) Two 3p electrons became unpaired, (ii) An electron was promoted from the 2p orbital to the 3s orbital, or (iii) An electron was promoted from the 3s orbital to the 3p orbital?
Ch.9 - Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
Chapter 9, Problem 7b
In the hydrocarbon (b) How many s bonds are there in the molecule?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the type of hydrocarbon (alkane, alkene, alkyne, or aromatic) to understand the bonding structure.
Count the number of carbon atoms in the molecule, as each carbon atom will have at least one sigma (s) bond with another carbon or a hydrogen atom.
Identify any functional groups or additional elements attached to the carbon chain and count the sigma bonds associated with them.
Remember that each single bond is a sigma bond, and in double or triple bonds, one of the bonds is a sigma bond.
Sum up all the sigma bonds from the carbon-carbon bonds, carbon-hydrogen bonds, and any other sigma bonds involving other atoms or groups.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. In hydrocarbons, these bonds primarily occur between carbon and hydrogen atoms. The type of covalent bond can be classified as single, double, or triple, depending on the number of shared electron pairs. Understanding the nature of these bonds is essential for determining the structure and properties of the hydrocarbon.
Recommended video:
Guided course
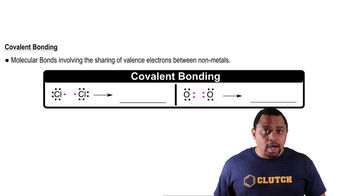
Chemical Bonds
Sigma (σ) Bonds
Sigma bonds are the strongest type of covalent bond formed by the head-on overlap of atomic orbitals. In hydrocarbons, each single bond between carbon and hydrogen or between carbon atoms is a sigma bond. Identifying the number of sigma bonds in a molecule is crucial for understanding its geometry and reactivity, as these bonds define the framework of the molecular structure.
Recommended video:
Guided course
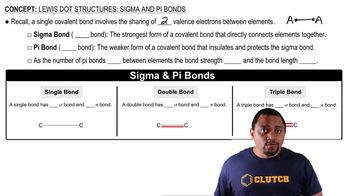
Lewis Dot Structures: Sigma & Pi Bonds
Hydrocarbon Structure
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds consisting solely of carbon and hydrogen atoms. They can be classified into aliphatic (linear or branched) and aromatic (cyclic) structures. The arrangement of these atoms and the types of bonds they form determine the physical and chemical properties of the hydrocarbon. Analyzing the structure helps in counting the number of sigma bonds present in the molecule.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Intro To Hydrocarbons
Related Practice
Textbook Question
624
views
Textbook Question
The orbital diagram that follows presents the final step in the formation of hybrid orbitals by a silicon atom. (b) What type of hybrid orbital is produced in this hybridization?
668
views
Textbook Question
In the hydrocarbon
(a) What is the hybridization at each carbon atom in the molecule?
597
views
Textbook Question
In the hydrocarbon
(d) Identify all the 120° bond angles in the molecule.
601
views
1
comments
Textbook Question
The drawing below shows the overlap of two hybrid orbitals to form a bond in a hydrocarbon. (a) Which of the following types of bonds is being formed: (i) C¬C s, (ii) C¬C p, or (iii) C¬H s?
464
views
Textbook Question
The drawing below shows the overlap of two hybrid orbitals to form a bond in a hydrocarbon. (b) Which of the following could be the identity of the hydrocarbon: (i) CH4, (ii) C2H6, (iii) C2H4, or (iv) C2H2?
763
views
