Textbook Question
Draw sketches illustrating the overlap between the following orbitals on two atoms: (a) the 2s orbital on each atom
586
views
1
rank
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

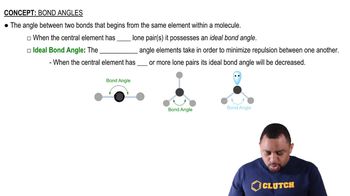

Draw sketches illustrating the overlap between the following orbitals on two atoms: (a) the 2s orbital on each atom
Draw sketches illustrating the overlap between the following orbitals on two atoms: (b) the 2pz orbital on each atom (assume both atoms are on the z-axis)
For each statement, indicate whether it is true or false. (d) Nonbonding electron pairs cannot occupy a hybrid orbital.
Consider the molecule BF3. (c) What hybrid orbitals should be constructed on the B atom to make the B–F bonds in BF3?
Consider the SCl2 molecule. (c) What hybrid orbitals should be constructed on the S atom to make the S-Cl bonds in SCl2?
Consider the SCl2 molecule.(d) What valence orbitals, if any, remain unhybridized on the S atom in SCl2?