Consider the Lewis structure for glycine, the simplest amino acid:
(b) What are the hybridizations of the orbitals on the two oxygens and the nitrogen atom, and what are the approximate bond angles at the nitrogen?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
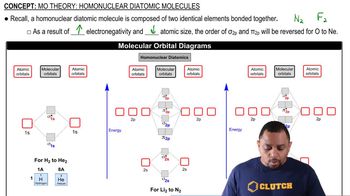


Consider the Lewis structure for glycine, the simplest amino acid:
(b) What are the hybridizations of the orbitals on the two oxygens and the nitrogen atom, and what are the approximate bond angles at the nitrogen?
Consider the Lewis structure for acetic acid, which is known as vinegar: (b) What are the hybridizations of the orbitals on the two oxygen atoms, and what are the approximate bond angles at the oxygen that is connected to carbon and hydrogen? What are the hybridizations of the orbitals on the two oxygen atoms?
Consider the Lewis structure for glycine, the simplest amino acid:
(c) What is the total number of s bonds in the entire molecule, and what is the total number of p bonds?
(c) Would you expect N2O to exhibit delocalized p bonding?
In the formate ion, HCO2-, the carbon atom is the central atom with the other three atoms attached to it. (c) Are there multiple equivalent resonance structures for the ion?
In the formate ion, HCO2-, the carbon atom is the central atom with the other three atoms attached to it. (d) How many electrons are in the p system of the ion?