In the Lewis structure shown here, A, D, E, Q, X, and Z represent elements in the first two rows of the periodic table. Identify all six elements so that the formal charges of all atoms are zero.
Ch.8 - Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
Chapter 8, Problem 7c
The partial Lewis structure that follows is for a hydrocarbon molecule. In the full Lewis structure, each carbon atom satisfies the octet rule, and there are no unshared electron pairs in the molecule. The carbon—carbon bonds are labeled 1, 2, and 3. (c) Which carbon—carbon bond is the strongest one?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
insert step 1: Understand that the strength of a carbon-carbon bond is related to the type of bond: single, double, or triple.
insert step 2: Recall that a single bond (sigma bond) is weaker than a double bond (one sigma and one pi bond), and a double bond is weaker than a triple bond (one sigma and two pi bonds).
insert step 3: Identify the types of carbon-carbon bonds present in the molecule by analyzing the partial Lewis structure.
insert step 4: Determine which bond is a single, double, or triple bond based on the number of shared electron pairs between the carbon atoms.
insert step 5: Conclude that the strongest carbon-carbon bond is the one with the most shared electron pairs, typically a triple bond.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Octet Rule
The octet rule is a chemical guideline stating that atoms tend to bond in such a way that they each have eight electrons in their valence shell, achieving a stable electron configuration similar to that of noble gases. In hydrocarbons, carbon atoms typically form four bonds to satisfy this rule, influencing the molecule's stability and reactivity.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Octet Rule
Types of Carbon-Carbon Bonds
Carbon atoms can form single, double, or triple bonds with each other, with each type having different strengths and characteristics. Single bonds (sigma bonds) are the weakest, while double bonds (one sigma and one pi bond) are stronger, and triple bonds (one sigma and two pi bonds) are the strongest. The bond strength affects the overall stability of the molecule.
Recommended video:
Guided course
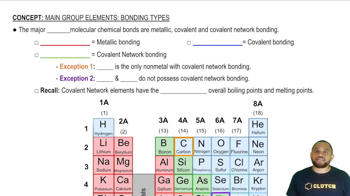
Bonding Types
Bond Strength and Length
Bond strength is inversely related to bond length; shorter bonds are generally stronger due to the increased overlap of atomic orbitals. In hydrocarbons, the presence of multiple bonds (double or triple) results in shorter bond lengths compared to single bonds, making them stronger. Understanding this relationship is crucial for determining which carbon-carbon bond is the strongest.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Average Bond Order
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1294
views
Open Question
Fill in the blank with the appropriate numbers for both electrons and bonds (considering that single bonds are counted as one, double bonds as two, and triple bonds as three). (a) Fluorine has _ valence electrons and makes _ bond(s) in compounds. (b) Oxygen has _ valence electrons and makes _ bond(s) in compounds. (c) Nitrogen has _ valence electrons and makes _ bond(s) in compounds. (d) Carbon has _ valence electrons and makes _ bond(s) in compounds.
Textbook Question
The partial Lewis structure that follows is for a hydrocarbon molecule. In the full Lewis structure, each carbon atom satisfies the octet rule, and there are no unshared electron pairs in the molecule. The carbon—carbon bonds are labeled 1, 2, and 3. (a) How many hydrogen atoms are in the molecule?
797
views
Textbook Question
Consider the Lewis structure for the polyatomic oxyanion shown here, where X is an element from the third period (Na - Ar). By changing the overall charge, n, from 1- to 2- to 3- we get three different polyatomic ions. For each of these ions (b) determine the formal charge of the central atom, X;
887
views
Textbook Question
(a) True or false: An element's number of valence electrons is the same as its atomic number.
844
views
Textbook Question
(b) How many valence electrons does a nitrogen atom possess?
700
views
