Moseley established the concept of atomic number by studying X rays emitted by the elements. The X rays emitted by some of the elements have the following wavelengths: Element Wavelength (pm) Ne 1461 Ca 335.8 Zn 143.5 Zr 78.6 Sn 49.1 (e) A particular element emits X rays with a wavelength of 98.0 pm. What element do you think it is?
Ch.7 - Periodic Properties of the Elements
Chapter 7, Problem 2
Which of these spheres represents F, which represents Br, and which represents Br-?


Verified Solution
Video duration:
54sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Atomic Radius
Atomic radius refers to the size of an atom, typically measured from the nucleus to the outer boundary of the surrounding cloud of electrons. In the periodic table, atomic radius generally increases down a group due to the addition of electron shells, while it decreases across a period from left to right due to increased nuclear charge, which pulls electrons closer to the nucleus.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Atomic Radius
Ionic Radius
Ionic radius is the measure of an atom's ion in a crystal lattice. Cations (positively charged ions) are smaller than their neutral atoms because they lose an electron, reducing electron-electron repulsion and allowing the remaining electrons to be pulled closer to the nucleus. Conversely, anions (negatively charged ions) are larger than their neutral atoms due to the addition of electrons, which increases repulsion among them.
Recommended video:
Guided course
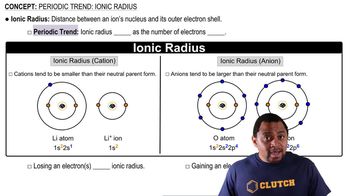
Ionic Radius
Periodic Trends
Periodic trends are patterns observed in the periodic table that illustrate how certain properties of elements change across periods and down groups. Key trends include atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity. Understanding these trends helps predict the behavior of elements, such as the relative sizes of F, Br, and Br-, which can be inferred from their positions in the periodic table.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Periodic Trends
Related Practice
Textbook Question
427
views
Textbook Question
Consider the Mg2+, Cl-, K+, and Se2- ions. The four spheres below represent these four ions, scaled according to ionic size. (b) In terms of size, between which of the spheres would you find the (i) Ca2+ and (ii) S2- ions?
1016
views
Textbook Question
In the following reaction
which sphere represents a metal and which represents a nonmetal?
370
views
1
rank
Textbook Question
Shown below is a qualitative diagram of the atomic orbital energies for an Na atom. The number of orbitals in each subshell is not shown.
(d) A sodium vapor lamp (Figure 7.23) operates by using electricity to excite the highest-energy electron to the next highest-energy level. Light is produced when the excited electron drops back to the lower level. Which two energy levels are involved in this process for the Na atom?
571
views
