An aqueous solution contains 1.2 mM of total ions. (a) If the solution is NaCl(aq), what is the concentration of chloride ion?
Ch.4 - Reactions in Aqueous Solution
Chapter 4, Problem 12
You are titrating an acidic solution with a basic one, and just realized you forgot to add the indicator that tells you when the equivalence point is reached. In this titration, the indicator turns blue at the equivalence point from an initially colorless solution. You quickly grab a bottle of indicator and add some to your titration beaker, and the whole solution turns dark blue. What do you do now?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
1. The dark blue color indicates that the solution has passed the equivalence point. This is because the indicator changes color when the solution changes from acidic to basic, which happens at the equivalence point. If the solution is dark blue, it means it is now basic.
2. The titration has gone too far, and you've added more base than needed to neutralize the acid. Therefore, you cannot accurately determine the concentration of the acid in the solution at this point.
3. To correct this, you will need to start the titration process over again. Dispose of the current solution safely according to your lab's guidelines.
4. Prepare a new sample of the acidic solution, ensuring it is the same volume and concentration as the original sample.
5. Before starting the titration, remember to add the indicator to the new solution. Then, proceed with the titration, adding the base slowly and carefully to avoid overshooting the equivalence point again.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Titration
Titration is a quantitative analytical technique used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution by reacting it with a solution of known concentration. In an acid-base titration, an acid reacts with a base, and the endpoint is indicated by a color change, often facilitated by an indicator. Understanding the titration process is crucial for interpreting results and determining the equivalence point.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Acid-Base Titration
Equivalence Point
The equivalence point in a titration is the stage at which the amount of titrant added is stoichiometrically equivalent to the amount of substance in the solution being titrated. This point is significant because it indicates that the reaction between the acid and base is complete. Identifying the equivalence point is essential for accurate calculations of concentration.
Recommended video:
Guided course

At the Equivalence Point
Indicators
Indicators are substances that change color at a specific pH range, signaling the completion of a reaction in titrations. In this scenario, the indicator turns blue at the equivalence point, providing a visual cue for the titration's progress. Choosing the appropriate indicator is vital, as it must change color at or near the pH of the equivalence point for accurate results.
Recommended video:
Guided course
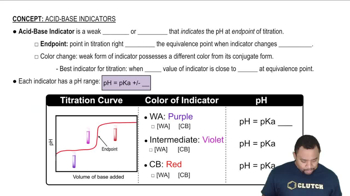
Acid-Base Indicators
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1142
views
Textbook Question
An aqueous solution contains 1.2 mM of total ions. (b) If the solution is FeCl3(aq), what is the concentration of chloride ion?
531
views
Textbook Question
Which data set, of the two graphed here, would you expect to observe from a titration like that shown in Figure 4.18?
286
views
Textbook Question
State whether each of the following statements is true or false. Justify your answer in each case. (a) Electrolyte solutions conduct electricity because electrons are moving through the solution.
516
views
Textbook Question
State whether each of the following statements is true or false. Justify your answer in each case. (b) If you add a nonelectrolyte to an aqueous solution that already contains an electrolyte, the electrical conductivity will not change.
987
views
Textbook Question
(a) Do colloids made only of gases exist? Why or why not?
124
views
