Bronze is a solid solution of Cu(s) and Sn(s); solutions of metals like this that are solids are called alloys. There is a range of compositions over which the solution is considered a bronze. Bronzes are stronger and harder than either copper or tin alone. (c) Suggest a reaction that you could do to remove all the tin from this bronze to leave a pure copper sample. Justify your reasoning.
Hard water contains Ca2+, Mg2+, and Fe2+, which interfere with the action of soap and leave an insoluble coating on the insides of containers and pipes when heated. Water softeners replace these ions with Na+. Keep in mind that charge balance must be maintained. (a) If 1500 L of hard water contains 0.020 M Ca2+ and 0.0040 M Mg2+, how many moles of Na+ are needed to replace these ions?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Ion Concentration and Molarity
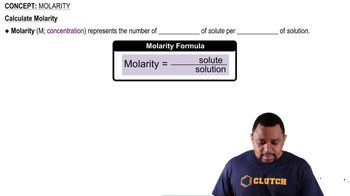
Charge Balance in Solutions

Stoichiometry in Chemical Reactions

Neurotransmitters are molecules that are released by nerve cells to other cells in our bodies, and are needed for muscle motion, thinking, feeling, and memory. Dopamine is a common neurotransmitter in the human brain. (c) Experiments with rats show that if rats are dosed with 3.0 mg/kg of cocaine (that is, 3.0 mg cocaine per kg of animal mass), the concentration of dopamine in their brains increases by 0.75 mM after 60 seconds. Calculate how many molecules of dopamine would be produced in a rat (average brain volume 5.00 mm3) after 60 seconds of a 3.0 mg/kg dose of cocaine.
Hard water contains Ca2+, Mg2+, and Fe2+, which interfere with the action of soap and leave an insoluble coating on the insides of containers and pipes when heated. Water softeners replace these ions with Na+. Keep in mind that charge balance must be maintained. (b) If the sodium is added to the water softener in the form of NaCl, how many grams of sodium chloride are needed?
Citric acid, C6H8O7, is a triprotic acid. It occurs naturally in citrus fruits like lemons and has applications in food flavouring and preservatives. A solution containing an unknown concentration of the acid is titrated with KOH. It requires 23.20 mL of 0.500 M KOH solution to titrate all three acidic protons in 100.00 mL of the citric acid solution. Write a balanced net ionic equation for the neutralization reaction.
Citric acid, C6H8O7, is a triprotic acid. It occurs naturally in citrus fruits like lemons and has applications in food flavouring and preservatives. A solution containing an unknown concentration of the acid is titrated with KOH. It requires 23.20 mL of 0.500 M KOH solution to titrate all three acidic protons in 100.00 mL of the citric acid solution. Calculate the molarity of the citric acid solution.
