Textbook Question
(a) What volume of 0.115 M HClO4 solution is needed to neutralize 50.00 mL of 0.0875 M NaOH?
987
views
1
rank
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

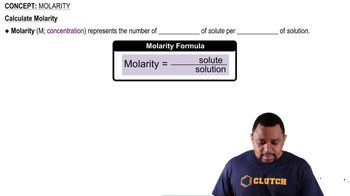

(a) What volume of 0.115 M HClO4 solution is needed to neutralize 50.00 mL of 0.0875 M NaOH?
(b) What volume of HCl is needed to neutralize 2.87 g of Mg(OH)2?
(d) If 45.3 mL of a 0.108 M HCl solution is needed to neutralize a solution of KOH, how many grams of KOH must be present in the solution?
(b) How many milliliters of 0.125 M H2SO4 are needed to neutralize 0.200 g of NaOH?
(c) If 55.8 mL of a BaCl2 solution is needed to precipitate all the sulfate ion in a 752-mg sample of Na2SO4, what is the molarity of the BaCl2 solution?