Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
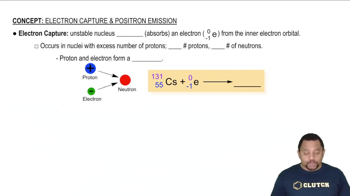
Electron Capture
Electron capture is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus captures an inner-shell electron, typically from the K-shell. This process results in the conversion of a proton into a neutron, leading to a decrease in the atomic number of the element while the mass number remains unchanged. It is a common decay mode for proton-rich isotopes, allowing them to achieve a more stable configuration.
Recommended video:
Nuclear Equations
Nuclear equations represent the transformation of one element into another during nuclear reactions, including decay processes. They are written to show the initial and final states of the nucleus, including the emission or absorption of particles. In these equations, the atomic number and mass number must be balanced, ensuring that the total number of protons and neutrons remains constant before and after the reaction.
Recommended video:
Selenium-72
Selenium-72 is a radioactive isotope of selenium with 34 protons and 38 neutrons, giving it a mass number of 72. It undergoes various decay processes, including electron capture, to achieve stability. Understanding its nuclear properties and behavior is essential for writing accurate nuclear equations, as it provides the necessary information about the starting material in the reaction.
Recommended video:
Hydrogen Compounds Example