In a series of experiments, a chemist prepared three different compounds that contain only iodine and fluorine and determined the mass of each element in each compound: Compound Mass of Iodine (g) Mass of Fluorine (g) 1 4.75 3.56 2 7.64 3.43 3 9.41 9.86 (a) Calculate the mass of fluorine per gram of iodine in Compound 3.
Give the name or chemical formula, as appropriate, for each of the following acids: (d) hypochlorous acid (e) iodic acid (f) sulfurous acid.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Acids and Their Nomenclature

Hypochlorous Acid

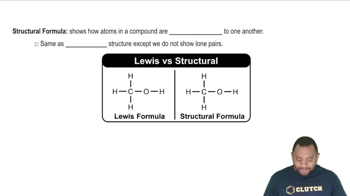
Chemical Formulas and Structure
Identify the element represented by each of the following symbols and give the number of protons and neutrons in each: (b) 12753X (c) 8636X (d) 6730X
Predict whether each of the following compounds is molecular or ionic: (f) K2O2 (g) PCl5
Provide the name or chemical formula, as appropriate, for each of the following acids: (a) hydroiodic acid (b) chloric acid (c) nitrous acid
Write the chemical formula for each substance mentioned in the following word descriptions (use the front inside cover to find the symbols for the elements you do not know). (b) On treatment with hydrofluoric acid, silicon dioxide forms silicon tetrafluoride and water. (use the front inside cover to find the symbols for the elements you do not know). (c) Sulfur dioxide reacts with water to form sulfurous acid. (use the front inside cover to find the symbols for the elements you do not know). (d) The substance phosphorus trihydride, commonly called phosphine, is a toxic gas. (e) Perchloric acid reacts with cadmium to form cadmium(II) perchlorate.
Give the name or chemical formula, as appropriate, for each of the following binary molecular substances: (c) XeO3 (d) dinitrogen tetroxide (e) hydrogen cyanide
