The first atoms of seaborgium (Sg) were identified in 1974. The longest-lived isotope of Sg has a mass number of 266. (b) Atoms of Sg are very unstable, and it is therefore difficult to study this element's properties. Based on the position of Sg in the periodic table, what element should it most closely resemble in its chemical properties?
Ch.2 - Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
Chapter 2, Problem 105
From the molecular structures shown here, identify the one that corresponds to each of the following species: (a) chlorine gas; (b) propane; (c) nitrate ion; (d) sulfur trioxide; (e) methyl chloride, CH3Cl.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the molecular structure of chlorine gas (Cl2). Chlorine gas consists of two chlorine atoms bonded together.
Identify the molecular structure of propane (C3H8). Propane consists of three carbon atoms bonded in a chain with eight hydrogen atoms attached.
Identify the molecular structure of the nitrate ion (NO3-). The nitrate ion consists of one nitrogen atom bonded to three oxygen atoms, with one of the bonds being a double bond.
Identify the molecular structure of sulfur trioxide (SO3). Sulfur trioxide consists of one sulfur atom bonded to three oxygen atoms, with all bonds being double bonds.
Identify the molecular structure of methyl chloride (CH3Cl). Methyl chloride consists of one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms and one chlorine atom.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molecular Structure
Molecular structure refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It determines the molecule's shape, bond angles, and overall geometry, which are crucial for understanding its chemical properties and reactivity. For example, the linear structure of chlorine gas (Cl2) contrasts with the tetrahedral structure of methane (CH4), influencing their interactions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Molecular Formula
Chemical Formula
A chemical formula represents the types and numbers of atoms in a molecule. It provides essential information about the composition of a substance, such as CH3Cl for methyl chloride, indicating one carbon, three hydrogens, and one chlorine atom. Understanding chemical formulas is vital for identifying and distinguishing between different compounds.
Recommended video:
Guided course
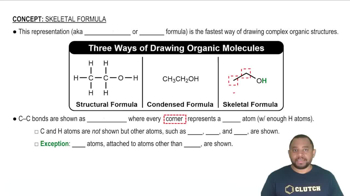
Skeletal Formula
Ionic vs. Covalent Compounds
Ionic compounds are formed through the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in charged ions, while covalent compounds involve the sharing of electrons. For instance, the nitrate ion (NO3-) is an ionic species, whereas propane (C3H8) is a covalent molecule. Recognizing the differences between these types of compounds helps in predicting their behavior and interactions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ionic Compounds Naming
Related Practice
Textbook Question
566
views
Open Question
The explosion of an atomic bomb releases many radioactive isotopes, including strontium-90. Considering the location of strontium in the periodic table, suggest a reason why this isotope is particularly dangerous for human health.
Open Question
Calculate the value of the silver in the American Silver Eagle coin, assuming its thickness is uniform, given that it has a diameter of 41 mm, a thickness of 2.5 mm, a silver density of 10.5 g/cm3, and the approximate market price of silver is $0.51 per gram.
Open Question
Name each of the following chlorides. Assuming that the compounds are ionic, what charge is associated with the metallic element in each case? (a) AgCl (b) TiCl₄ (c) IrCl₃ (d) LiCl.
Textbook Question
Fill in the blanks in the following table:
Cation Anion Formula Name
Lithium oxide
Fe2+ PO43-
Al2(SO4)3
Copper(II) nitrate
Cr3+ I−
MnClO2
Ammonium carbonate
Zinc perchlorate
Complete the first column of the table.
863
views
Textbook Question
Fill in the blanks in the following table:
Cation Anion Formula Name
Lithium oxide
Fe2+ PO43-
Al2(SO4)3
Copper(II) nitrate
Cr3+ I−
MnClO2
Ammonium carbonate
Zinc perchlorate
Complete the third column of the table.
Complete the fourth column of the table.
805
views
