Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Solubility Product Constant (Ksp)
The solubility product constant (Ksp) is an equilibrium constant that applies to the solubility of sparingly soluble ionic compounds. It represents the product of the molar concentrations of the ions, each raised to the power of their coefficients in the balanced equation. For Mn(OH)2, Ksp can be used to determine the conditions under which the compound will precipitate, particularly in relation to pH and ion concentration.
Recommended video:
Solubility Product Constant
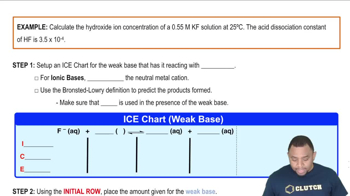
pH and Hydroxide Ion Concentration
pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, defined as the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration. In the context of precipitating Mn(OH)2, increasing the pH leads to a higher concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-), which can react with Mn2+ ions to form the insoluble compound. Understanding the relationship between pH and hydroxide ion concentration is crucial for controlling precipitation.
Recommended video:
Hydroxide Ion Concentration Example
Concentration Units and Dilution
Concentration units, such as parts per billion (ppb), are essential for quantifying the amount of a substance in a solution. In this case, achieving a concentration of Mn2+ less than 1 mg/L (1 ppb) requires careful calculation of the necessary pH to ensure that the solubility of Mn(OH)2 is exceeded. Understanding how to convert and manipulate concentration units is vital for solving the problem effectively.
Recommended video: