Write the chemical equation and the Kb expression for the reaction of each of the following bases with water: (c) benzoate ion, C6H5CO2-
Codeine 1C18H21NO32 is a weak organic base. A 5.0 * 10-3M solution of codeine has a pH of 9.95. Calculate the value of Kb for this substance. What is the pKb for this base?

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Weak Bases and pH
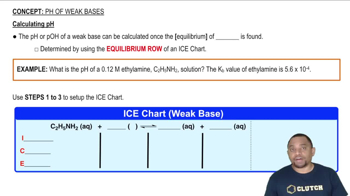
Equilibrium Constant (Kb)

Relationship between Kb and pKb

Ephedrine, a central nervous system stimulant, is used in nasal sprays as a decongestant. This compound is a weak organic base: C10H15ON1aq2 + H2O1l2 Δ C10H15ONH+1aq2 + OH-1aq2 A 0.035 M solution of ephedrine has a pH of 11.33. (a) What are the equilibrium concentrations of C10H15ON, C10H15ONH+, and OH-?
Ephedrine, a central nervous system stimulant, is used in nasal sprays as a decongestant. This compound is a weak organic base: C10H15ON1aq2 + H2O1l2 Δ C10H15ONH+1aq2 + OH-1aq2 A 0.035 M solution of ephedrine has a pH of 11.33. (b) Calculate Kb for ephedrine.
Use the acid-dissociation constants in Table 16.3 to arrange these oxyanions from strongest base to weakest: SO42-, CO32-, SO32-, and PO43-.
Given that Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 * 10-5 and that for hypochlorous acid is 3.0 * 10-8, which is the stronger acid?
Which is the stronger base, the acetate ion or the hypochlorite ion?
