At 20 °C, the vapor pressure of benzene (C6H6) is 75 torr, and that of toluene (C7H8) is 22 torr. Assume that benzene and toluene form an ideal solution. (a) What is the composition in mole fraction of a solution that has a vapor pressure of 35 torr at 20 °C?
List the following aqueous solutions in order of increasing boiling point: 0.120 m glucose, 0.050 m LiBr, 0.050 m Zn(NO3)2.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Colligative Properties
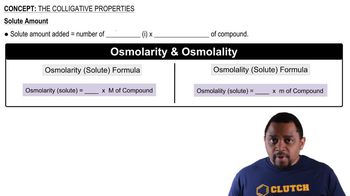
Boiling Point Elevation

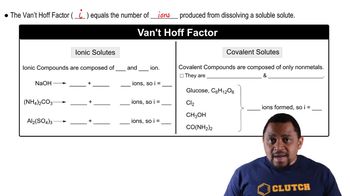
Van 't Hoff Factor (i)
At 20 °C, the vapor pressure of benzene (C6H6) is 75 torr, and that of toluene (C7H8) is 22 torr. Assume that benzene and toluene form an ideal solution. (b) What is the mole fraction of benzene in the vapor above the solution described in part (a)?
Using data from Table 13.3, calculate the freezing and boiling points of each of the following solutions: (a) 0.22 m glycerol (C3H8O3) in ethanol, (b) 0.240 mol of naphthalene (C10H8) in 2.45 mol of chloroform, (c) 1.50 g NaCl in 0.250 kg of water, (d) 2.04 g KBr and 4.82 g of glucose (C6H12O6) in 188 g of water.
Using data from Table 13.3, calculate the freezing and boiling points of each of the following solutions: (a) 0.25 m glucose in ethanol; (b) 20.0 g of decane, C10H22, in 50.0 g CHCl3; (c) 3.50 g NaOH in 175 g of water, (d) 0.45 mol ethylene glycol and 0.15 mol KBr in 150 g H2O.
