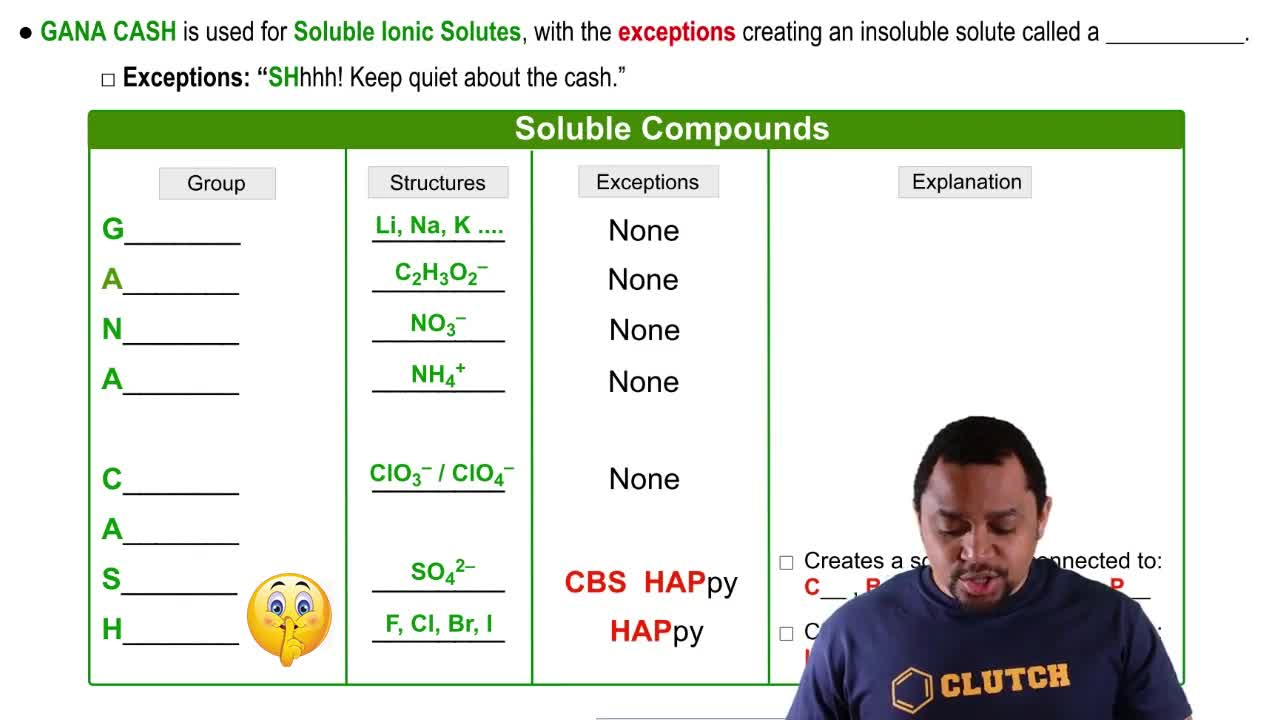
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Solubility
Solubility is the maximum amount of a solute that can dissolve in a given quantity of solvent at a specific temperature. It is typically expressed in grams of solute per 100 grams of solvent. Understanding solubility is crucial for determining whether a solution can become saturated, meaning no more solute can dissolve in the solvent.
Recommended video:
Saturated Solution
A saturated solution is one in which the maximum amount of solute has been dissolved in the solvent at a given temperature and pressure. When additional solute is added to a saturated solution, it will not dissolve and will remain undissolved. Identifying whether a solution is saturated is essential for predicting the behavior of solutes in a solvent.
Recommended video:
Types of Aqueous Solutions
Ionic Compounds and Their Solubility
Ionic compounds, such as Pb(NO3)2, dissociate into their constituent ions when dissolved in water. The solubility of these compounds varies widely based on their chemical nature and the temperature of the solvent. Knowledge of the solubility rules for ionic compounds helps predict whether a specific ionic solid will dissolve in water, which is key to answering the question about saturation.
Recommended video: