CuI, CsI, and NaI each adopt a different type of structure. The three different structures are those shown in Figure 12.26. (a) Use ionic radii, Cs+ 1r = 1.81 A 2, Na+ 1r = 1.16 A 2, Cu+ 1r = 0.74 A 2, and, I- 1r = 2.06 A 2, to predict which compound will crystallize with which structure.
Ch.12 - Solids and Modern Materials

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 12, Problem 66a
The coordination number for the Al3+ ion is typically between four and six. Use the anion coordination number to determine the Al3 + coordination number in the following compounds: (a) AlF3 where the fluoride ions are two coordinate.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the coordination number of the fluoride ions, which is given as two.
Understand that the coordination number of the cation (Al^{3+}) is determined by the number of anions it is bonded to.
In AlF_3, each fluoride ion is bonded to two Al^{3+} ions, indicating a bridging role.
Calculate the total number of fluoride ions surrounding one Al^{3+} ion by considering the stoichiometry of the compound.
Conclude that the coordination number of Al^{3+} is determined by the number of fluoride ions it coordinates with, based on the structure of AlF_3.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Coordination Number
The coordination number refers to the number of ligand atoms that are bonded to a central metal ion in a coordination complex. It is a crucial concept in coordination chemistry, as it influences the geometry and stability of the complex. For example, a coordination number of four typically leads to a tetrahedral arrangement, while six results in an octahedral geometry.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Coordination Numbers
Ligands
Ligands are ions or molecules that can donate a pair of electrons to a central metal ion, forming coordinate covalent bonds. They can vary in their ability to coordinate, with some being monodentate (binding through one atom) and others being polydentate (binding through multiple atoms). The nature and number of ligands significantly affect the properties and reactivity of the metal complex.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ligands Example
Anion Coordination
Anion coordination refers to the arrangement and bonding of anions around a central cation in a coordination compound. The coordination number of the cation can be influenced by the coordination number of the anions. In the case of AlF3, where fluoride ions have a coordination number of two, this suggests that the aluminum ion can effectively coordinate with multiple fluoride ions, leading to a specific overall coordination number for Al3+.
Recommended video:
Guided course
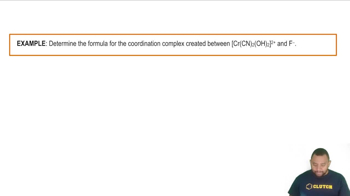
Coordination Complexes Example
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1211
views
Textbook Question
The coordination number for the Al3+ ion is typically between four and six. Use the anion coordination number to determine the Al3 + coordination number in the following compounds: (b) Al2O3 where the oxygen ions are six coordinate.
539
views
Textbook Question
The coordination number for the Al3+ ion is typically between four and six. Use the anion coordination number to determine the Al3 + coordination number in the following compounds: (c) AlN where the nitride ions are four coordinate.
1240
views
