Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Liquid Crystalline Phase
The liquid crystalline phase is a state of matter that exhibits properties of both liquids and solid crystals. In this phase, molecules are organized in a way that allows for some fluidity while maintaining a degree of order, which can lead to unique optical and mechanical properties. This organization can affect how the substance flows and interacts with its environment.
Recommended video:
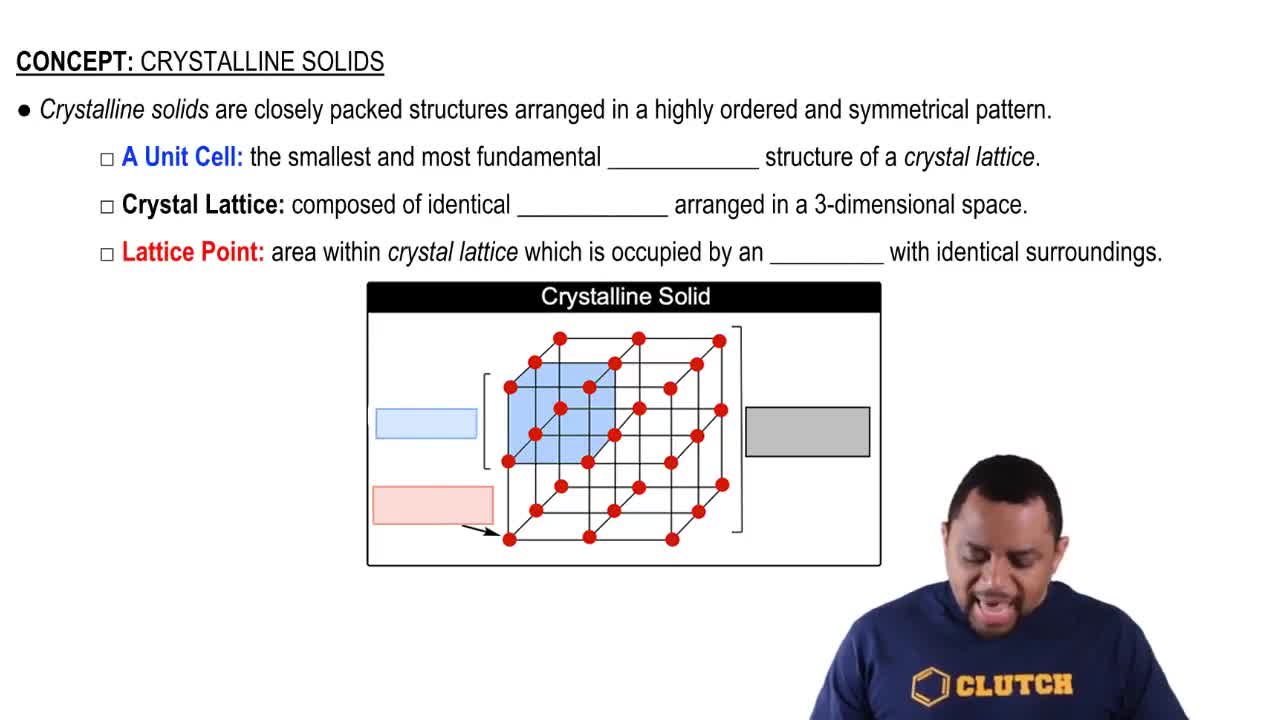
Crystalline Solids Structure
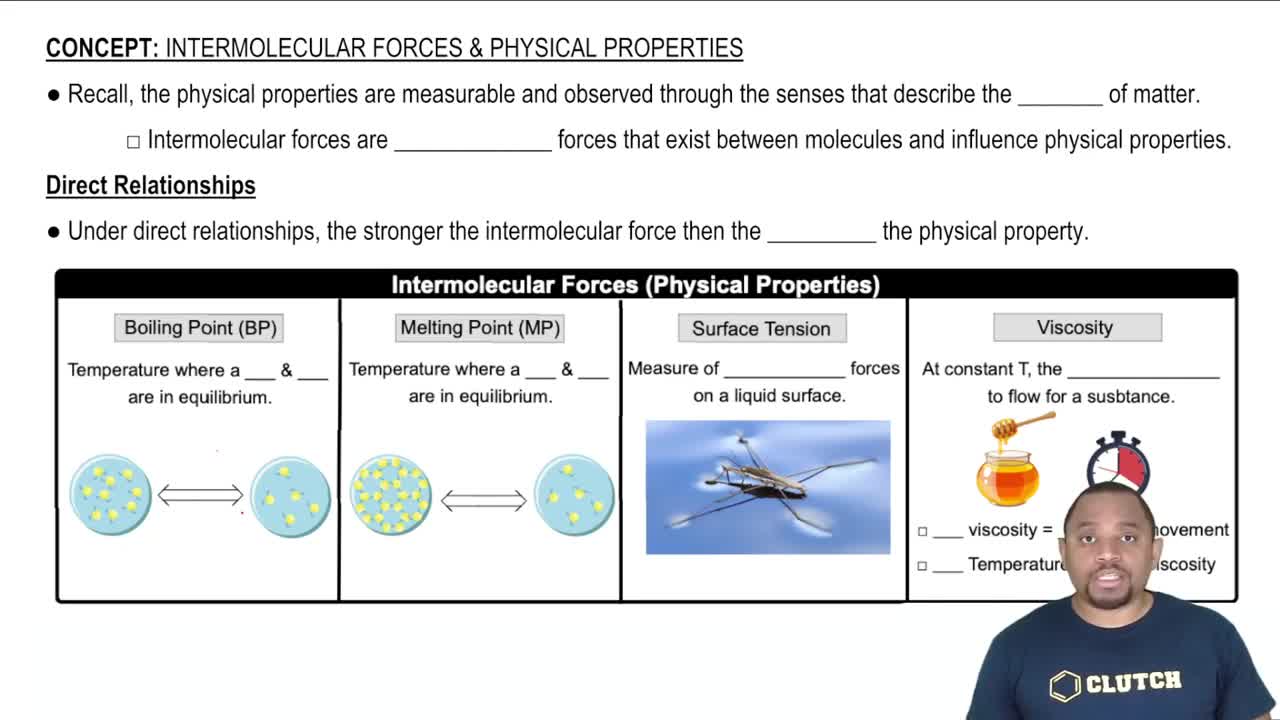
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow. It is influenced by factors such as temperature, molecular structure, and intermolecular forces. A higher viscosity indicates a thicker fluid that flows more slowly, while a lower viscosity indicates a thinner fluid that flows more easily. Understanding viscosity is crucial for comparing the flow characteristics of different phases of a substance.
Recommended video:
Intermolecular Forces and Properties
Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces are the attractive forces between molecules that influence their physical properties, including viscosity. In the liquid crystalline phase, these forces can be stronger or more organized due to the alignment of molecules, leading to increased resistance to flow compared to the more randomly arranged molecules in the liquid phase. This difference in molecular arrangement directly impacts the viscosity of the substance.
Recommended video:
Intermolecular vs Intramolecular Forces
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance