Judge the following statements as true or false. If you believe a statement to be false, provide a corrected version. (f) A hypothesis is more weakly supported by experimental evidence than a theory.
Ch.1 - Introduction: Matter, Energy, and Measurement
Chapter 1, Problem 93
You are assigned the task of separating a desired granular material with a density of 3.62 g/cm3 from an undesired granular material that has a density of 2.04 g/cm3. You want to do this by shaking the mixture in a liquid in which the heavier material will fall to the bottom and the lighter material will float. A solid will float on any liquid that is more dense. Using an Internet-based source or a handbook of chemistry, find the densities of the following substances: carbon tetrachloride, hexane, benzene, and diiodomethane. Which of these liquids will serve your purpose, assuming no chemical interaction takes place between the liquid and the solids?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the densities of the given liquids: carbon tetrachloride, hexane, benzene, and diiodomethane.
Compare the density of each liquid to the densities of the granular materials: 3.62 g/cm^3 (desired) and 2.04 g/cm^3 (undesired).
Determine which liquid has a density greater than 2.04 g/cm^3 but less than 3.62 g/cm^3.
The liquid with a density in this range will allow the undesired material to float and the desired material to sink.
Select the liquid that meets these criteria for effective separation of the materials.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Density
Density is defined as mass per unit volume, typically expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³). It is a crucial property that determines whether an object will float or sink in a fluid. An object will float in a liquid if its density is less than that of the liquid. In this scenario, understanding the densities of the granular materials and the liquids is essential for effective separation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Density Concepts
Buoyancy
Buoyancy is the upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of an object immersed in it. This principle explains why objects with lower density than the fluid will float, while those with higher density will sink. In the context of the question, selecting a liquid with a density lower than the desired material (3.62 g/cm³) but higher than the undesired material (2.04 g/cm³) is key to achieving separation through buoyancy.
Separation Techniques
Separation techniques in chemistry involve methods used to isolate specific components from a mixture based on their physical properties. In this case, the technique of density-based separation is employed, where shaking the mixture in a suitable liquid allows for the separation of materials based on their differing densities. Understanding various separation methods is important for selecting the most effective approach for the task at hand.
Recommended video:
Guided course
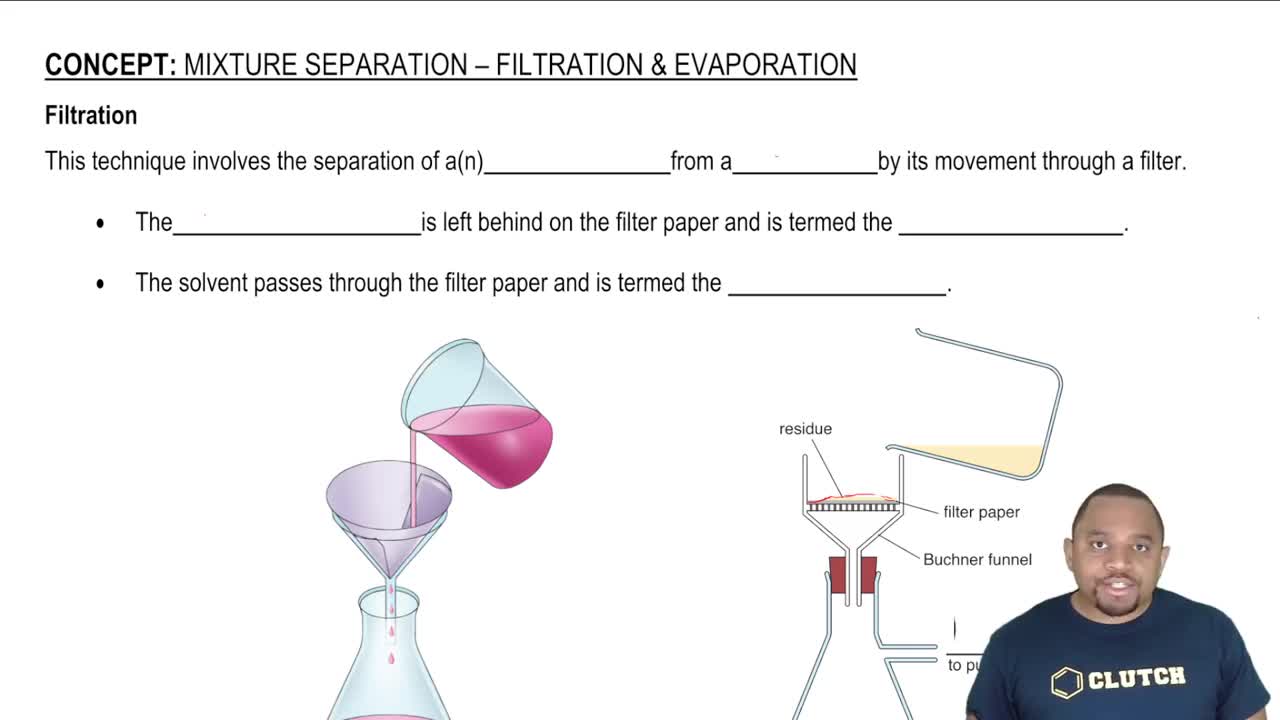
Filtration and Evaporation
Related Practice
Textbook Question
520
views
Textbook Question
Judge the following statements as true or false. If you believe a statement to be false, provide a corrected version. (g) The number 0.0033 has more significant figures than 0.033.
394
views
Textbook Question
Judge the following statements as true or false. If you believe a statement to be false, provide a corrected version. (i) Compounds always contain at least two different elements.
628
views
Textbook Question
In 2009, a team from Northwestern University and Western Washington University reported the preparation of a new 'spongy' material composed of nickel, molybdenum, and sulfur that excels at removing mercury from water. The density of this new material is 0.20 g/cm3, and its surface area is 1242 m2 per gram of material. (b) Calculate the surface area for a 10.0-mg sample of this material.
696
views
Textbook Question
U.S. 1-cent coin (a penny) has a diameter of 19 mm and a
thickness of 1.5 mm. Assume the coin is made of pure copper,
whose density and approximate market price are 8.9 g/cm3
and $2.40 per pound, respectively. Calculate the value of
the copper in the coin, assuming its thickness is uniform.
2383
views
Textbook Question
(c) Using the
volume of a silver atom and the formula for the volume of a
sphere, calculate the radius in angstroms of a silver atom.
753
views
