What type of quantity (for example, length, volume, density) do the following units indicate? (g) Pa.
Ch.1 - Introduction: Matter, Energy, and Measurement
Chapter 1, Problem 72g
"Give the derived SI units for each of the following quantities in base SI units: (g) energy = mass ⨉ (velocity)2

Verified Solution
Video duration:
53sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
SI Units
The International System of Units (SI) is a standardized system of measurement used globally in science and engineering. It is based on seven base units, including the meter for length, kilogram for mass, and second for time. Derived units are formed from these base units to measure other quantities, such as energy, which is expressed in joules.
Recommended video:
Guided course

SI Units
Energy
Energy is the capacity to do work or produce heat and is a fundamental concept in physics and chemistry. In the context of mechanics, energy can be expressed as the product of mass and the square of velocity, represented mathematically as E = m × v². The derived SI unit for energy is the joule (J), which is equivalent to one kilogram meter squared per second squared (kg·m²/s²).
Recommended video:
Guided course
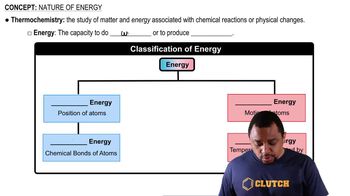
Nature of Energy
Derived Units
Derived units are combinations of base SI units that describe physical quantities. For example, energy is a derived unit that combines mass (kilograms), length (meters), and time (seconds) to form joules. Understanding how to derive these units from base units is essential for solving problems in physics and chemistry, as it allows for the conversion and manipulation of different measurements.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ideal Gas Law Derivations
Related Practice
Textbook Question
409
views
Textbook Question
Give the derived SI units for each of the following quantities in base SI units: (a) acceleration = distance/time2
458
views
Textbook Question
Give the derived SI units for each of the following quantities in base SI units: (e) power = work/time
1141
views
Textbook Question
The distance from Earth to the Moon is approximately 240,000 mi. (a) What is this distance in meters?
1321
views
Textbook Question
The distance from Earth to the Moon is approximately 240,000 mi. (b) The peregrine falcon has been measured as traveling up to 350 km/ hr in a dive. If this falcon could fly to the Moon at this speed, how many seconds would it take?
762
views
Textbook Question
The distance from Earth to the Moon is approximately 240,000 mi. (c) The speed of light is 3.00 ⨉ 108 m/s. How long does it take for light to travel from Earth to the Moon and back again?
616
views
