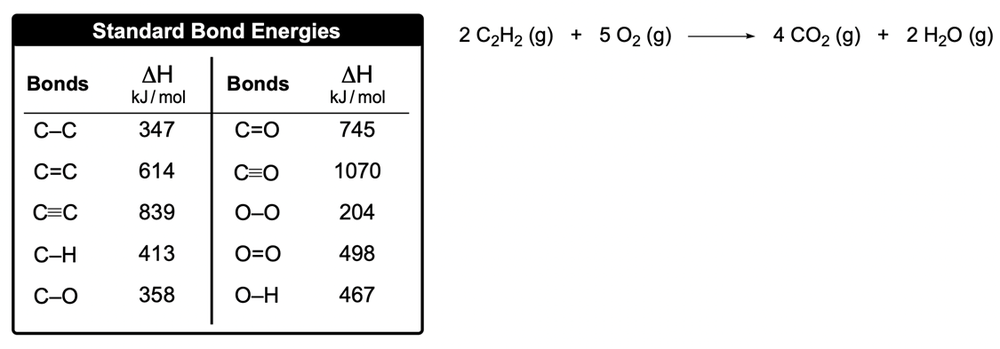
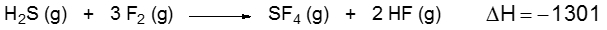Bond energy, also known as bond enthalpy and represented as ΔHbe, refers to the amount of energy stored in the bonds between atoms in a molecule. This concept is crucial for calculating the enthalpy of reaction (ΔHreaction), which is sometimes referred to as the heat of reaction. Understanding the distinction between endothermic and exothermic processes is essential in this context.
In an endothermic process, energy is absorbed to break a bond, resulting in a positive ΔH value, indicating a gain of energy. Conversely, in an exothermic process, energy is released when bonds are formed, leading to a negative ΔH value, signifying a loss of energy.
When calculating the enthalpy of reaction using individual bond enthalpies, the formula is:
ΔHreaction = Σ (Bond Energies of Reactants) - Σ (Bond Energies of Products)
This means that you sum the bond energies of the reactants and subtract the sum of the bond energies of the products. It's important to note that this approach is different from using the enthalpy of formation for a compound, where the formula is:
ΔHreaction = Σ (Enthalpy of Formation of Products) - Σ (Enthalpy of Formation of Reactants)
In summary, when working with bond enthalpies, always remember to apply the reactants minus products formula to determine the enthalpy of reaction accurately.