Textbook Question
Identify each solid as molecular, ionic, or atomic. a. Ar(s) b. H2O(s) c. K2O(s) d. Fe(s)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
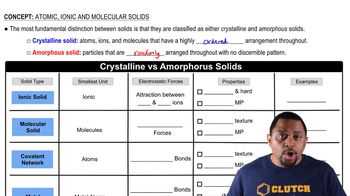


Identify each solid as molecular, ionic, or atomic. a. Ar(s) b. H2O(s) c. K2O(s) d. Fe(s)
Identify each solid as molecular, ionic, or atomic. a. CaCl2(s)
Identify each solid as molecular, ionic, or atomic. b. CO2(s)
Which solid has the highest melting point? Why? Ar(s), CCl4(s), LiCl(s), CH3OH(s)
Which solid has the highest melting point? Why? C(s, diamond), Kr(s), NaCl(s), H2O(s)
Which solid in each pair has the higher melting point and why?
a. TiO2(s) or HOOH(s)
b. CCl4(s) or SiCl4(s)
c. Kr(s) or Xe(s)