A 1.0-g sample of carbon dioxide (CO2) is fully decomposed into its elements, yielding 0.273 g of carbon and 0.727 g of oxygen. (a) What is the ratio of the mass of O to C?
Sodium reacts with oxygen in air to form two compounds: sodium oxide and sodium peroxide. In forming sodium oxide, 23.0 g of sodium combines with 8.0 g of hydrogen. In forming sodium peroxide, 23.0 g of sodium combines with 16.0 g of oxygen. (a) What are the mass ratios of oxygen in the two compounds?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceRecommended similar problem, with video answer:

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Stoichiometry

Mass Ratio

Chemical Formula
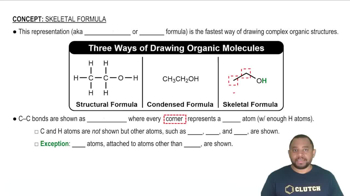
A 1.0-g sample of carbon dioxide (CO2) is fully decomposed into its elements, yielding 0.273 g of carbon and 0.727 g of oxygen. (b) If a sample of a different compound decomposes into 0.429 g of carbon and 0.571 g of oxygen, what is its ratio of the mass of O to C?
A 1.0-g sample of carbon dioxide (CO2) is fully decomposed into its elements, yielding 0.273 g of carbon and 0.727 g of oxygen. If a sample of a different compound decomposes into 0.429 g of carbon and 0.571 g of oxygen, what is its ratio of the mass of O to C? (c) According to Dalton's atomic theory, what is the empirical formula of the second compound?
Sodium reacts with oxygen in air to form two compounds: sodium oxide and sodium peroxide. In forming sodium oxide, 23.0 g of sodium combines with 8.0 g of hydrogen. In forming sodium peroxide, 23.0 g of sodium combines with 16.0 g of oxygen. (b) What fundamental law does this experiment demonstrate?
A chemist finds that 30.82 g of nitrogen will react with 17.60, 35.20, 70.40, or 88.00 g of oxygen to form four different compounds. (a) Calculate the mass of oxygen per gram of nitrogen in each compound. 30.82 g N and 17.60 g O
A chemist finds that 30.82 g of nitrogen will react with 17.60, 35.20, 70.40, or 88.00 g of oxygen to form four different compounds. (a) Calculate the mass of oxygen per gram of nitrogen in each compound. 30.82 g N and 88.00 g O
