Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ionization Energy
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion in its gaseous state. For alkali metals, which have one valence electron, this energy is relatively low, allowing them to easily lose that electron and form positive ions. The lower the ionization energy, the more reactive the metal, particularly in reactions with halogens like chlorine.
Recommended video:
Reactivity of Alkali Metals
Alkali metals (Group 1 elements) are known for their high reactivity, which increases down the group. This is due to the decreasing ionization energy as the atomic size increases, making it easier for these metals to lose their outermost electron. When reacting with halogens, such as chlorine, the most reactive alkali metal will typically form a more stable ionic compound, releasing energy in the process.
Recommended video:
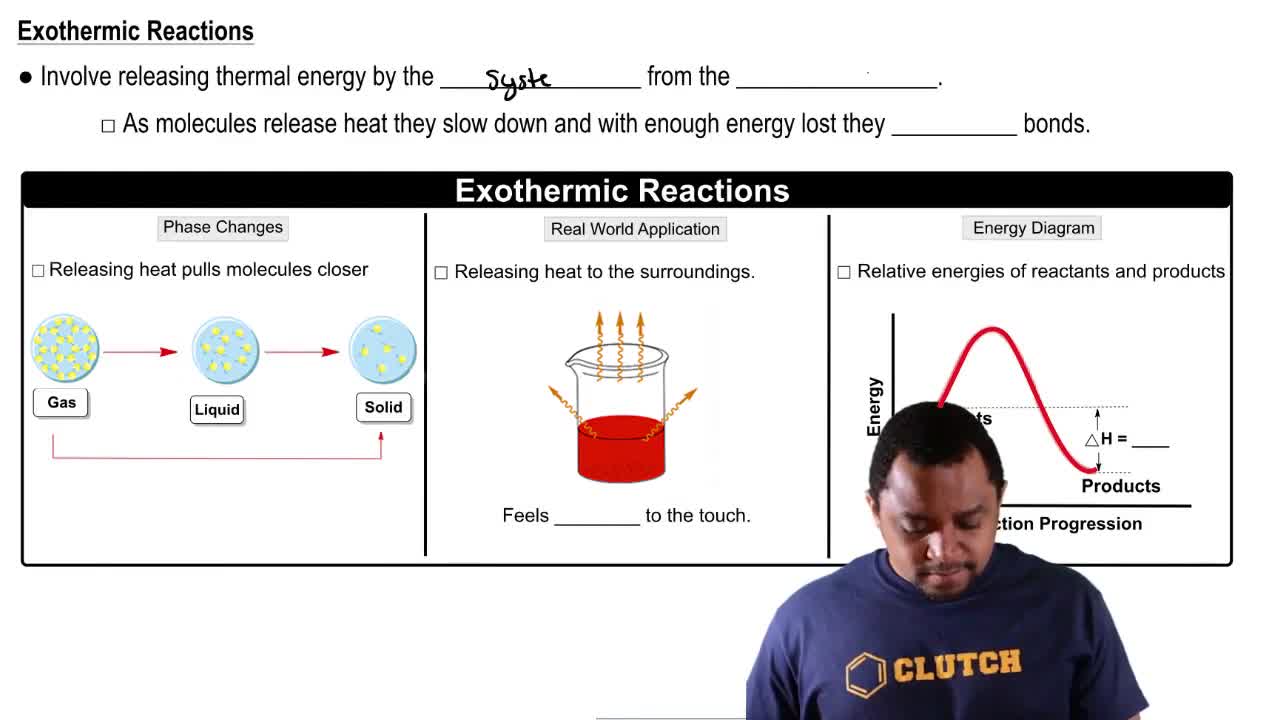
Exothermic Reactions
An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that releases energy, usually in the form of heat, to the surroundings. In the context of alkali metals reacting with chlorine gas, the formation of ionic bonds between the metal cation and the chloride anion releases significant energy. The more exothermic the reaction, the more stable the resulting compound, which is influenced by the reactivity of the alkali metal involved.
Recommended video:
Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance