Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It is determined by the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons around the central atom, which influence the shape due to repulsion between electron pairs. Understanding molecular geometry is crucial for predicting the physical and chemical properties of a substance.
Recommended video:
Molecular Geometry with Two Electron Groups
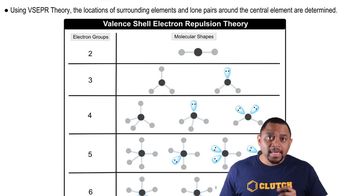
VSEPR Theory
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a model used to predict the geometry of molecules based on the repulsion between electron pairs in the valence shell of the central atom. According to VSEPR, electron pairs will arrange themselves to minimize repulsion, leading to specific molecular shapes. For BrF5, the presence of five bonding pairs and one lone pair results in a square pyramidal geometry.
Recommended video:
Molecular Shapes and VSEPR
Bond Conventions in Molecular Sketching
Bond conventions in molecular sketching involve using specific symbols and notations to represent atoms, bonds, and lone pairs in a molecule. Common conventions include solid lines for bonds in the plane, dashed lines for bonds going behind the plane, and wedged lines for bonds coming out of the plane. These conventions help accurately depict the three-dimensional structure of molecules like BrF5 when sketching.
Recommended video:
 Tro 4th Edition
Tro 4th Edition Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory
Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory Problem 4
Problem 4 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance