What role does EDTA4- play as a trace additive to mayonnaise? Would the glycinate ion (H2NCH2CH2NH2) be an effective substitute for EDTA4-?
Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry
All textbooks McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry
Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry Problem 21.79a
Problem 21.79a
 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry
Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry Problem 21.79a
Problem 21.79aChapter 21, Problem 21.79a
Assign a systematic name to each of the following ions.
(a) [AuCl4]-
(b) [Fe(CN)6]4-
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
<insert step 1> Identify the central metal atom in each complex ion. For (a), the central metal is Au (gold), and for (b), it is Fe (iron).
<insert step 2> Determine the oxidation state of the central metal atom. For (a), consider the charge of the ligands (Cl is -1) and the overall charge of the ion (-1) to find the oxidation state of Au. For (b), consider the charge of the ligands (CN is -1) and the overall charge of the ion (-4) to find the oxidation state of Fe.
<insert step 3> Name the ligands. For (a), the ligand is chloride, and for (b), the ligand is cyanide. Use the appropriate prefixes if there are multiple identical ligands (e.g., tetra- for four chloride ions).
<insert step 4> Combine the ligand names with the metal name. For anionic complexes, the metal name ends with the suffix '-ate'. For (a), use 'aurate' for gold, and for (b), use 'ferrate' for iron.
<insert step 5> Write the systematic name by placing the ligand names first, followed by the metal name with its oxidation state in Roman numerals in parentheses.>

Verified Solution
Video duration:
0m:0sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Coordination Compounds
Coordination compounds consist of a central metal atom or ion bonded to surrounding molecules or ions, known as ligands. The nature of these ligands and their arrangement around the metal center significantly influence the properties and reactivity of the compound. Understanding the structure of coordination compounds is essential for naming them systematically.
Recommended video:
Guided course
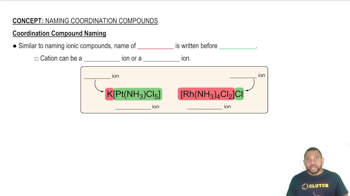
Coordination Compound Naming
Oxidation States
The oxidation state of an element in a compound indicates the degree of oxidation or reduction it has undergone. In coordination compounds, the oxidation state of the central metal ion is crucial for determining the systematic name. For example, in [AuCl4]-, gold has an oxidation state of +3, which is important for naming the ion correctly.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Oxidation Numbers
IUPAC Nomenclature
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) provides systematic rules for naming chemical compounds, including coordination complexes. The naming convention involves identifying the ligands, their quantities, and the oxidation state of the metal. For instance, in [Fe(CN)6]4-, the complex is named hexacyanoferrate(II) based on these rules.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Rules for Naming Alkanes
Related Practice
Textbook Question
70
views
Textbook Question
What is the systematic name for each of the following ions?
(a) [MnCl4]2-
(b) [Ni(NH3)6]2+
132
views
Textbook Question
What is the systematic name for each of the following ions?
(c) [Co(CO3)3]3-
(d) [Pt(en)2(SCN)2]2+
117
views
Textbook Question
Assign a systematic name to each of the following ions.
(c) [Fe(H2O)5NCS]2+
(d) [Cr(NH3)2(C2O4)2]-
220
views
Textbook Question
Based on the wavelength of maximum absorption of the cobalt complexes, arrange the following ligands in a spectrochemical series from weakest-field to strongest-field ligand.
(a) Cl- < NCS- < H2O < NH3
(b) Cl- < NCS- < H2O < NH3
(c) H2O < Cl- < NH3 < NCS-
(d) Cl- < H2O < NCS- < NH3
105
views
Textbook Question
What is the systematic name for each of the following coordination compounds?
(c) [Co(NH3)4Br2]Br
(d) Cu(gly)2
170
views