Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Hybridization
Hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals that can accommodate the bonding requirements of a molecule. In the case of benzyne, the two triply bonded carbon atoms are expected to exhibit sp hybridization, which involves the mixing of one s orbital and one p orbital, resulting in two sp hybrid orbitals that are oriented linearly.
Recommended video:
Bond Angles
Theoretical bond angles are determined by the hybridization of the atoms involved. For sp hybridized carbon atoms, the ideal bond angle is 180 degrees, as the hybrid orbitals are arranged linearly. In benzyne, the presence of the triple bond influences the geometry, leading to bond angles that may deviate slightly from the ideal due to steric and electronic effects.
Recommended video:
Reactivity of Benzyne
Benzyne is highly reactive due to the presence of a triple bond between two carbon atoms, which creates significant electron density and strain in the molecule. This reactivity is further enhanced by the instability of the benzyne structure, making it prone to undergo various chemical reactions, such as nucleophilic attacks, to relieve the strain and achieve a more stable configuration.
Recommended video:
Physical Properties Example
 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.8 - Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure
Ch.8 - Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure Problem 71
Problem 71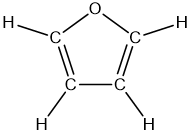
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance