Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Resonance Structures
Resonance structures are different ways of drawing a molecule that represent the same arrangement of atoms but differ in the distribution of electrons. In molecules like ortho-dichlorobenzene, resonance helps to illustrate how electrons are delocalized across the structure, affecting stability and reactivity. These structures are not real, but rather a way to visualize the electron distribution in a molecule.
Recommended video:
Delocalization of Electrons
Delocalization of electrons refers to the phenomenon where electrons are not confined to a single bond or atom but are spread out over several atoms. In ortho-dichlorobenzene, the presence of resonance allows for the electrons in the π system to be shared among multiple carbon atoms, which contributes to the molecule's stability and influences its chemical properties.
Recommended video:
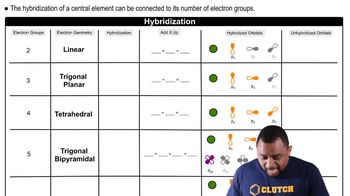
Molecular Geometry and Hybridization
Molecular geometry and hybridization describe the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals. In ortho-dichlorobenzene, the carbon atoms are sp² hybridized, leading to a planar structure that allows for effective overlap of p orbitals, facilitating resonance. Understanding these concepts is crucial for visualizing the molecule's shape and predicting its behavior in chemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Hybridization and Electron Geometry