It is common in mass spectrometry to assume that the mass of a cation is the same as that of its parent atom. (b) What percentage of the mass of an 1H atom does the electron represent?
The first atoms of seaborgium (Sg) were identified in 1974. The longest-lived isotope of Sg has a mass number of 266. (b) Atoms of Sg are very unstable, and it is therefore difficult to study this element's properties. Based on the position of Sg in the periodic table, what element should it most closely resemble in its chemical properties?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
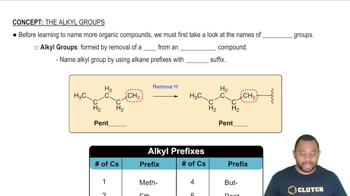
Key Concepts
Periodic Table Trends

Chemical Similarity and Group Characteristics
Isotopes and Stability

From the following list of elements—Mg, Li, Tl, Pb, Se, Cl, Xe, Si, C—pick the one that best fits each description. Use each element only once: (a) an alkali metal, (b) an alkaline earth metal, (c) a noble gas, (d) a halogen, (e) a metalloidin group 14, (f) a nonmetal listed in group 14, (g) a metal that forms a 3+ ion, (h) a nonmetal that forms a 2- ion, (i) an element that is used as radiation shielding.
The first atoms of seaborgium (Sg) were identified in 1974. The longest-lived isotope of Sg has a mass number of 266. (a) How many protons, electrons, and neutrons are in an 266Sg atom?
From the molecular structures shown here, identify the one that corresponds to each of the following species: (a) chlorine gas; (b) propane; (c) nitrate ion; (d) sulfur trioxide; (e) methyl chloride, CH3Cl.
