Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lewis Structures
Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the bonding between atoms in a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist. They help visualize the arrangement of electrons and the connectivity of atoms, which is crucial for understanding molecular geometry and reactivity. In the case of ibuprofen, completing the Lewis structure involves adding hydrogen atoms and lone pairs to satisfy the octet rule for each atom.
Recommended video:
Lewis Dot Structures: Ions
Octet Rule
The octet rule is a chemical rule of thumb that states atoms tend to bond in such a way that they each have eight electrons in their valence shell, achieving a stable electron configuration similar to that of noble gases. This rule is essential for determining how many hydrogen atoms need to be added to the ibuprofen structure to ensure that all carbon and oxygen atoms fulfill their octet requirements, leading to a stable molecule.
Recommended video:
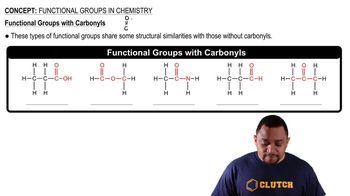
Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. In ibuprofen, the presence of carboxylic acid and aromatic functional groups influences its properties and biological activity. Understanding these groups is important for predicting how ibuprofen interacts with biological systems and how to accurately represent its structure.
Recommended video:
Carbonyl Functional Groups