Textbook Question
Draw an MO energy diagram for CO. (Use the energy ordering of O2.) Predict the bond order and make a sketch of the lowest energy bonding molecular orbital.
2540
views
1
comments
 Tro 4th Edition
Tro 4th Edition Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory
Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory Problem 84
Problem 84 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
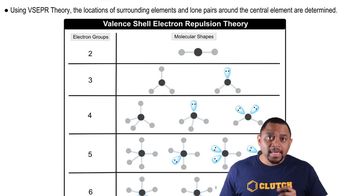

Draw an MO energy diagram for CO. (Use the energy ordering of O2.) Predict the bond order and make a sketch of the lowest energy bonding molecular orbital.
Draw an energy diagram for HCl. Predict the bond order and make a sketch of the lowest energy bonding molecular orbital.
The genetic code is based on four different bases with the structures shown here. Assign a geometry and hybridization to each interior atom in these four bases. d. guanine
The structure of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) is shown here. How many π bonds are present in acetylsalicylic acid?
The structure of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) is shown here. How many sigma bonds?