Textbook Question
The phase diagram for sulfur is shown here. The rhombic and monoclinic states are two solid states with different structures. b. Which of the two solid states of sulfur is more dense?
525
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
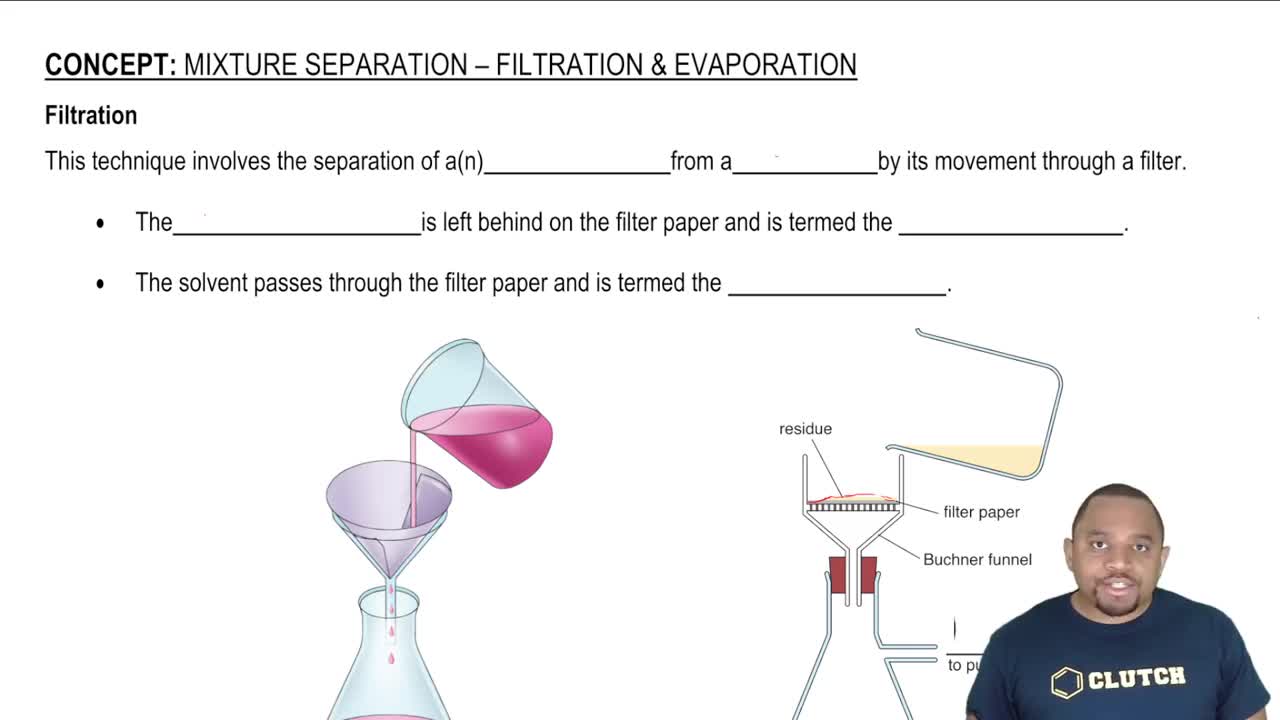

The phase diagram for sulfur is shown here. The rhombic and monoclinic states are two solid states with different structures. b. Which of the two solid states of sulfur is more dense?
Water is a good solvent for many substances. What is the molecular basis for this property, and why is it significant?
Explain the observed trend in the melting points of the hydrogen halides.
HI -50.8 °C
HBr -88.5 °C
HCl -114.8 °C
HF -83.1 °C
Explain the observed trend in the boiling points of these compounds.
H2Te -2 °C
H2Se -41.5 °C
H2S -60.7 °C
H2O 100 °C