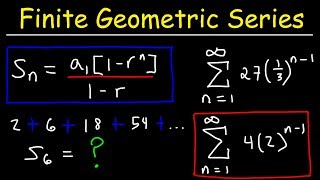
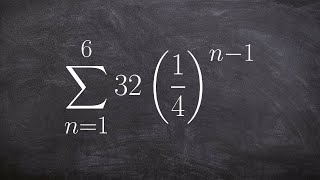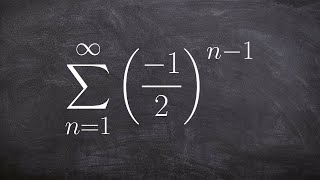9. Sequences, Series, & Induction
Geometric Sequences
9. Sequences, Series, & Induction
Geometric Sequences
Additional 9 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 12 of 12 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Write a recursive formula for the geometric sequence .
878views1rank - Multiple Choice
Find the term of the geometric sequence in which and .
596views - Multiple Choice
Write a formula for the general or term of the geometric sequence where and .
663views - Textbook Question
Write the first five terms of each geometric sequence. a1 = 5, r = 3
838views - Textbook Question
Write the first five terms of each geometric sequence. a1 = 20, r = 1/2
836views - Textbook Question
Write the first five terms of each geometric sequence. an = - 4a(n-1), a1 = 10
692views - Textbook Question
Write the first five terms of each geometric sequence. an = - 4a(n-1), a1 = 10
692views