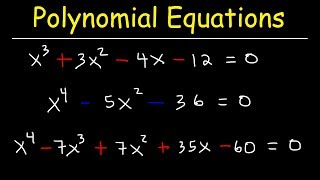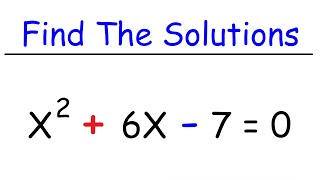4. Polynomial Functions
Zeros of Polynomial Functions
4. Polynomial Functions
Zeros of Polynomial Functions
Use Rational Zero Theorem to Find Possible Rational Zeros
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1–8, use the Rational Zero Theorem to list all possible rational zeros for each given function. f(x)=x^3+x^2−4x−4324views
- Textbook QuestionDetermine whether each statement is true or false. If false, explain why. The product of a complex number and its conjugate is always a real number.256views
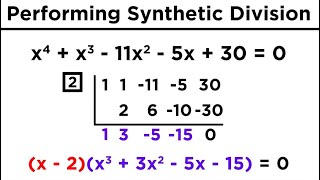
- Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 9–16, a) List all possible rational zeros. b) Use synthetic division to test the possible rational zeros and find an actual zero. c) Use the quotient from part (b) to find the remaining zeros of the polynomial function. f(x)=x^3+x^2−4x−4323views
- Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 9–16, a) List all possible rational zeros. b) Use synthetic division to test the possible rational zeros and find an actual zero. c) Use the quotient from part (b) to find the remaining zeros of the polynomial function. f(x)=x^3−2x^2−11x+12601views
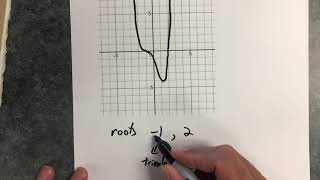
Find Zeros of a Polynomial Function
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Textbook QuestionDetermine whether each statement is true or false. If false, explain why. The polynomial function ƒ(x)=2x^5+3x^4-8x^3-5x+6 has three variations in sign.187views
- Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1–8, use the Rational Zero Theorem to list all possible rational zeros for each given function. f(x)=x^5−x^4−7x^3+7x^2−12x−12335views
- Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 9–16, a) List all possible rational zeros. b) Use synthetic division to test the possible rational zeros and find an actual zero. c) Use the quotient from part (b) to find the remaining zeros of the polynomial function. f(x)=x^3+4x^2−3x−6250views
- Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 17–24, a) List all possible rational roots. b) List all possible rational roots. c) Use the quotient from part (b) to find the remaining roots and solve the equation. x^3−2x^2−11x+12=0276views
Solve Polynomial Equations
Additional 1 creators.
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Textbook QuestionDetermine whether each statement is true or false. If false, explain why. A polynomial function having degree 6 and only real coefficients may have no real zeros.460views
- Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1–8, use the Rational Zero Theorem to list all possible rational zeros for each given function. f(x)=3x^4−11x^3−3x^2−6x+8224views
- Textbook QuestionUse the factor theorem and synthetic division to determine whether the second polynomial is a factor of the first. See Example 1. 4x^2+2x+54; x-4379views
- Textbook QuestionUse the factor theorem and synthetic division to determine whether the second polynomial is a factor of the first. See Example 1. x^3+2x^2+3; x-1432views
Use the Linear Factorization Theorem to Find Polynomials With Given Zeros
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Textbook QuestionDetermine whether each statement is true or false. If false, explain why. For ƒ(x)=(x+2)^4(x-3), the number 2 is a zero of multiplicity 4.273views1rank
- Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1–8, use the Rational Zero Theorem to list all possible rational zeros for each given function. f(x)=4x^4−x^3+5x^2−2x−6242views
- Textbook QuestionUse the factor theorem and synthetic division to determine whether the second polynomial is a factor of the first. See Example 1. x^3+6x^2-2x-7; x+1161views
- Textbook QuestionIf ƒ(x) is a polynomial function with real coefficients, and if 7+2i is a zero of the function, then what other complex number must also be a zero?274views
Use Descartes's Rule of Signs
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Textbook QuestionDetermine whether each statement is true or false. If false, explain why. Because x-1 is a factor of ƒ(x)=x^6-x^4+2x^2-2, we can also conclude that ƒ(1)=0205views
- Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1–8, use the Rational Zero Theorem to list all possible rational zeros for each given function. f(x)=3x^4−11x^3−x^2+19x+6210views
- Textbook QuestionUse the factor theorem and synthetic division to determine whether the second polynomial is a factor of the first. See Example 1. x^3-5x^2+3x+1; x-1152views
- Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 9–16, a) List all possible rational zeros. b) Use synthetic division to test the possible rational zeros and find an actual zero. c) Use the quotient from part (b) to find the remaining zeros of the polynomial function. f(x)=2x^3−3x^2−11x+6194views